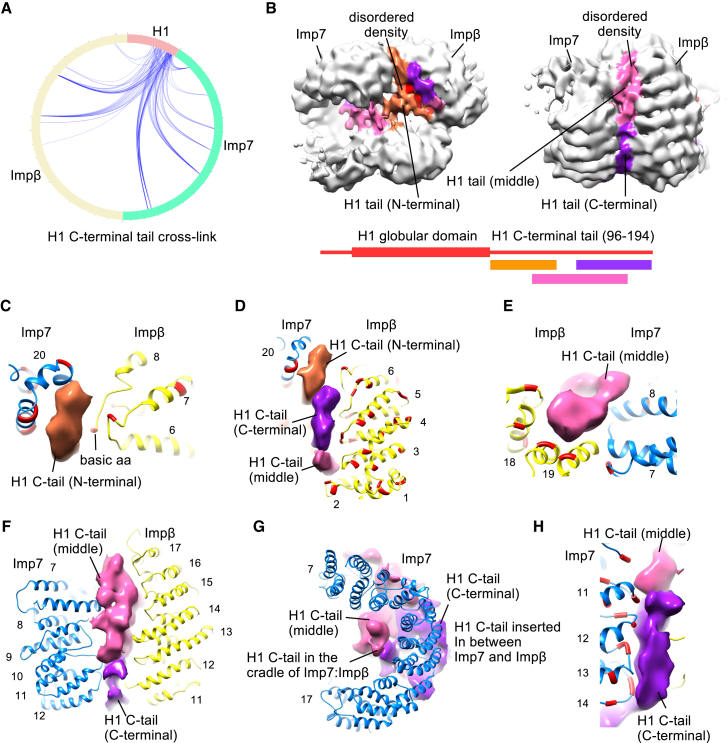
Figure 2.
A Disordered Region of H1 Shapes the Imp7:Impβ:H1.0 Complex
(A) Circular plot showing zero-length cross-links of the H1 C-terminal tail to Impβ and Imp7. Each Imp7 and Impβ residue cross-links to many lysines in the H1 C-terminal tail. The cross-links are shown in our Mendeley Data.
(B) The disordered density in the cradle and between two importins was segregated based on the cross-linking and mass spectrometry data. The density in proximity to the importin residues that cross-link predominantly to the N-terminal part of the H1 C-terminal tail is shown in orange, the middle part in pink, and the C-terminal part in violet. Contour level, ∼0.025.
(C) Close-up view of Imp7 HEAT repeat 20 and Impβ HEAT repeats 6 and 7. The N-terminal part of the H1 C-terminal tail inserts between the Impβ and Imp7 HEAT repeats and mediates interaction. The lysine-rich H1 tail interacts with the negatively charged residues (red) in the importins. Contour level, ∼0.025.
(D) Acidic residues (red) in the inner loops of Impβ N-terminal HEAT repeats 1–6 interact with the middle and C-terminal parts of the H1 C-terminal tail. Contour level, ∼0.025.
(E) Close-up view of Imp7 HEAT repeat 7 and Impβ HEAT repeats 18 and 19. The middle part of the H1 C-terminal tail inserts between the Impβ and Imp7 HEAT repeats and mediates interaction. The H1 tail interacts with the negatively charged residues (red) in the importins in the region. Contour level, ∼0.025.
(F) The middle and C-terminal parts of the H1 C-terminal tail insert between Impβ HEAT repeats 11–17 and Imp7 HEAT repeats 7–12. The disordered H1 tail holds the two importins together.
(G) The middle part of the H1 C-terminal tail is partially localized in the cradle formed by Impβ and Imp7. Contour level, ∼0.025.
(H) Acidic residues (red) in the inner loops of Imp7 HEAT repeats 11–14 interact with the middle and C-terminal parts of the H1 C-terminal tail. Contour level, ∼0.025.
See also Figure S5.