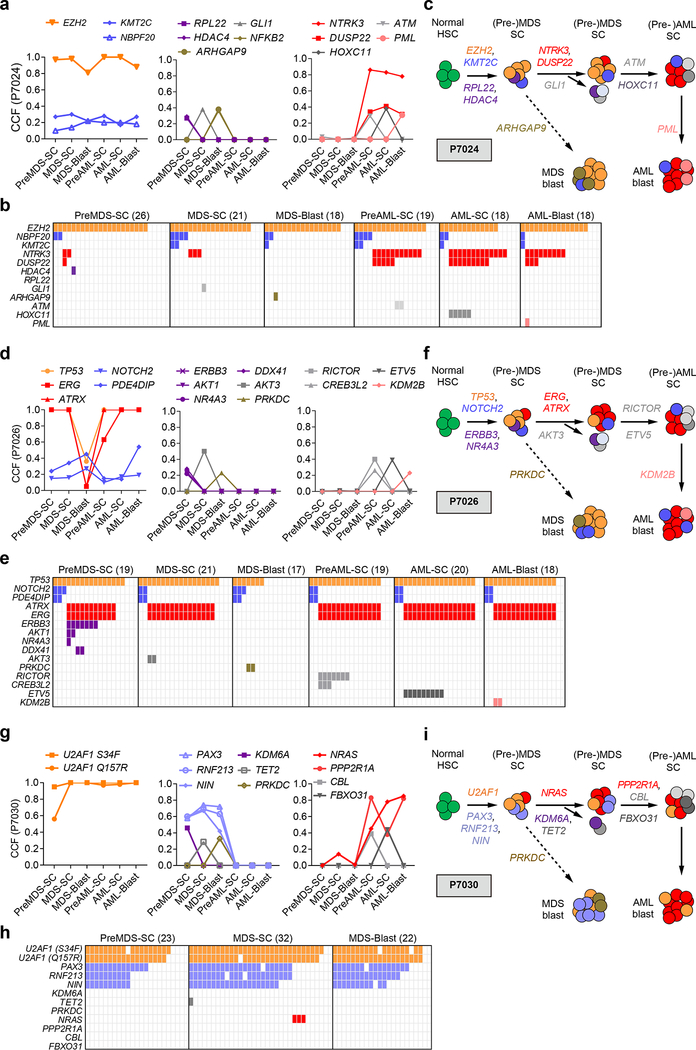
Fig. 3 |. Spatiotemporal subclonal evolution during the progression from MDS to sAML determined by single cell sequencing of sorted stem and blast cells.
a, CCFs of shared (left), MDS-specific (middle), AML specific (right) mutations across all cell populations in patient P7024. b, Single cell targeted sequencing of mutations across different cell populations of patient P7024. Each column represents the sequencing results of one single cell of the indicated cell population (preMDS-SC, MDS-SC, MDS-blasts, preAML-SC, AML-SC, AML-blasts), and the number of single cells tested in each population is shown in parentheses. The occurrence of a mutation in a single cell is indicated with the same color as in (a). c, Schematic model of clonal evolution in different stem and blast cell populations in patient P7024. Mutations in EZH2 were acquired early in the founding clone at the MDS stage, and acquisition of additional mutations in NTRK3 and DUSP22 contributed to the progression to sAML, while MDS blasts were characterized by different co-mutations. In this patient sAML developed from a rare subclone contained within MDS stem cells, and not through further evolution of MDS blasts. d, CCFs of shared (left), MDS-specific (middle), AML specific (right) mutations across all cell populations in patient P7026. e, Single cell targeted sequencing of mutations across different cell populations of patient P7026. f, Schematic model of clonal evolution in different stem and blast cell populations in patient P7026. Data again indicate that the dominant clone present in sAML stem and blast cells developed from a clone within the MDS stem cells that was nearly undetectable in MDS blast, indicating a crucial role of MDS stem cells in sAML initiation. g, CCFs of shared (left), MDS-specific (middle), AML-specific (right) mutations in different stem and blast populations at the MDS and sAML stage of patient P7030. h, Single cell targeted sequencing of mutations across different cell populations of patient P7030. i, Schematic model of clonal evolution in different stem and blast cell populations in patient P7030. Subclones of MDS stem cells with early founding mutations (i.e. U2AF1) remained present during MDS blast generation as well as AML progression, whereas other mutations, e.g. PAX3, RNF213, NIN and KDM6A, only occurred in MDS but not during progression to sAML. Progression to sAML originated from a subclone of MDS stem cells with NRAS mutation.