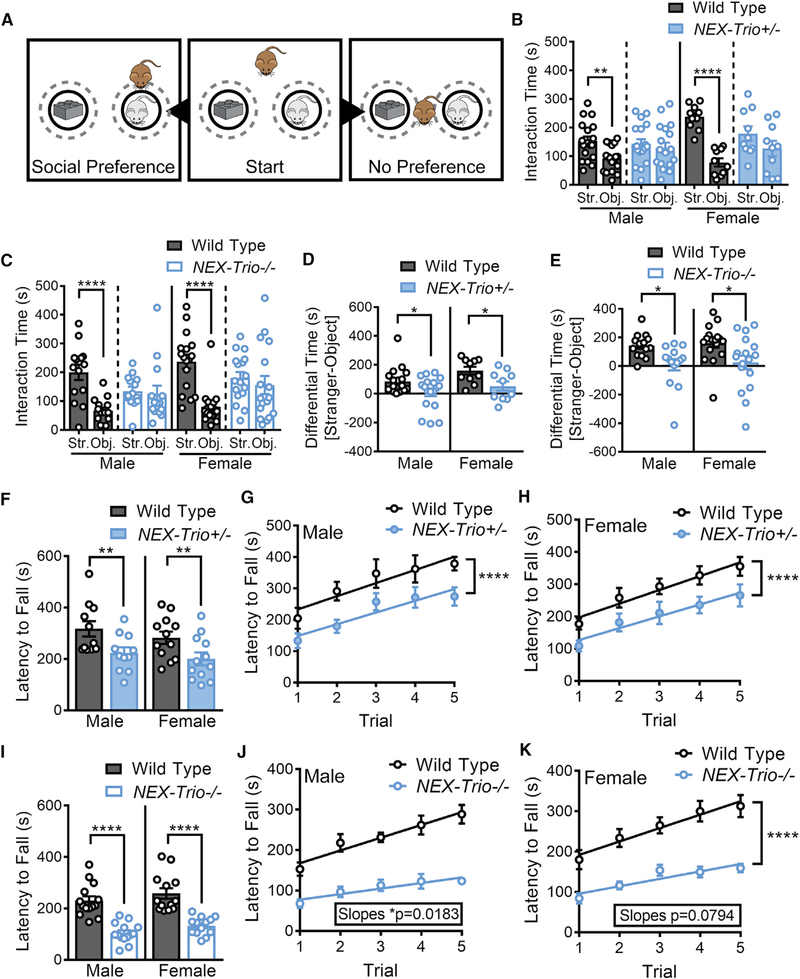
Figure 3. NEX–Trio+/− and NEX–Trio−/− Mice Do Not Show a Preference for Social Interaction and Show Decreased Motor Coordination.
(A) (Middle) In the social preference task, a test mouse (brown) is placed in an open field with a male stranger mouse (gray) and an object (Duplo blocks, similar color and size as the stranger mouse). (Left) Test mice that display social preference spend more time with the stranger mouse relative to the object. (Right) Test mice that display no preference spend equal time with the stranger mouse and object. Target zones are designated by the gray dotted circles.
(B and C) NEX–Trio+/− (B) and NEX–Trio−/− (C) mice did not show preference for the stranger mouse (Str.) relative to the object (Obj.), whereas WT mice displayed normal social preference. A linear regression with post hoc Bonf MC test identified differences (n = 10–18 littermate pairs).
(D and E) The difference in occupancy time between the social and nonsocial zones showed that NEX–Trio+/− (D) and NEX–Trio−/− (E) mice had reduced preference for the social zone compared to sex–matched WT littermates. RM two–way ANOVA with post hoc Bonf MC test identified differences (n = 10–18 littermate pairs).
(F and I) NEX–Trio+/− (F) and NEX–Trio−/− (I) mice of both sexes had a shorter latency to fall off of the accelerating rotarod than WT littermates. RM two–way ANOVA with post hoc Bonf MC test identified differences (n = 11–14 littermate pairs).
(G and H) Male (G) and female (H) NEX–Trio+/− mice had a shorter latency to fall off of the accelerating rotarod than WT littermates in every trial (difference in intercepts), but all groups learned at a rate of 40 s per trial (no difference in slopes).
(J and K) Male (J) and female (K) NEX–Trio−/− mice showed impaired motor learning (significant or suggestive difference in slopes) compared to WT littermates. Male and female WT mice learned at a rate of 32 and 33 s per trial, respectively; male and female NEX–Trio−/− mice learned at a rate of 14 and 18 s per trial, respectively. Linear regressions with post hoc test for differences between slopes and changes in intercepts identified differences (n = 11–14 littermate pairs).
See also Figures S2, S3, S4, and S5. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001).