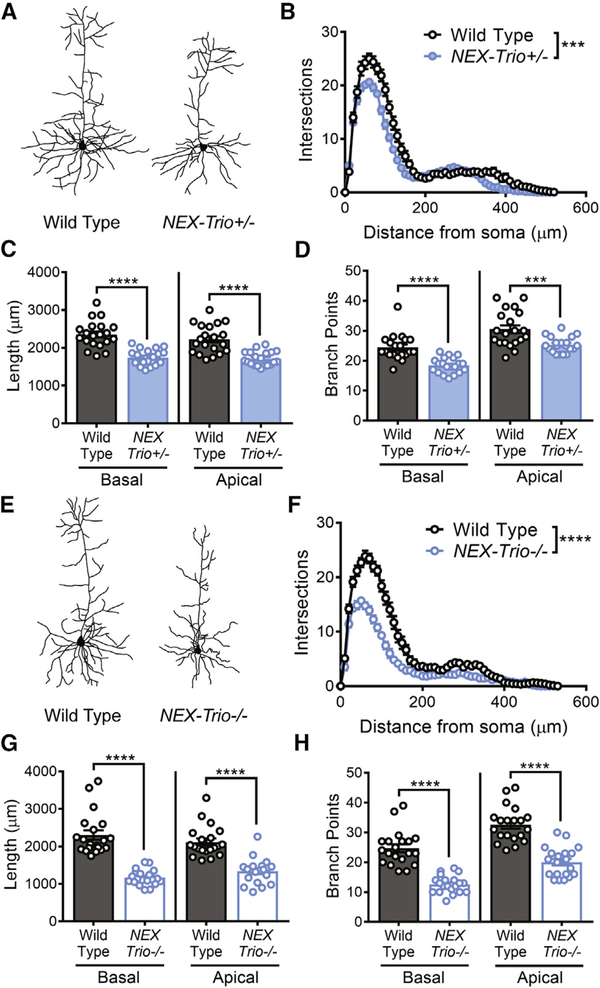
Figure 4. Dendritic Arborization Is Reduced in the Motor Cortex of NEX–Trio+/− and NEX–Trio−/− Mice.
(A and E) Representative dendritic arbor reconstructions are shown for layer 5 pyramidal neurons (L5 PNs) in NEX–Trio+/− (A) and NEX–Trio−/− (E) mice. (B and F) Sholl analysis revealed decreased dendritic arborization on L5 PNs in NEX–Trio+/− (B) and NEX–Trio−/− (F) mice relative to WT controls; the phenotype was more severe in NEX–Trio−/− mice (F). RM two–way ANOVA with post hoc Bonf MC test identified differences (n = 20 neurons from 4 mice per genotype).
(C and G) Apical and basal dendrite length were reduced on L5 PNs in NEX–Trio+/− (C) and NEX–Trio−/− (G) mice relative to WT controls.
(D and H) The numbers of apical and basal branch points were reduced on L5 PNs in NEX–Trio+/− (D) and NEX–Trio−/− (H) mice relative to WT controls. Unpaired t tests identified differences between groups (n = 20 neurons from 4 mice per genotype).
See also Figure S6. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001).