Figure 4.
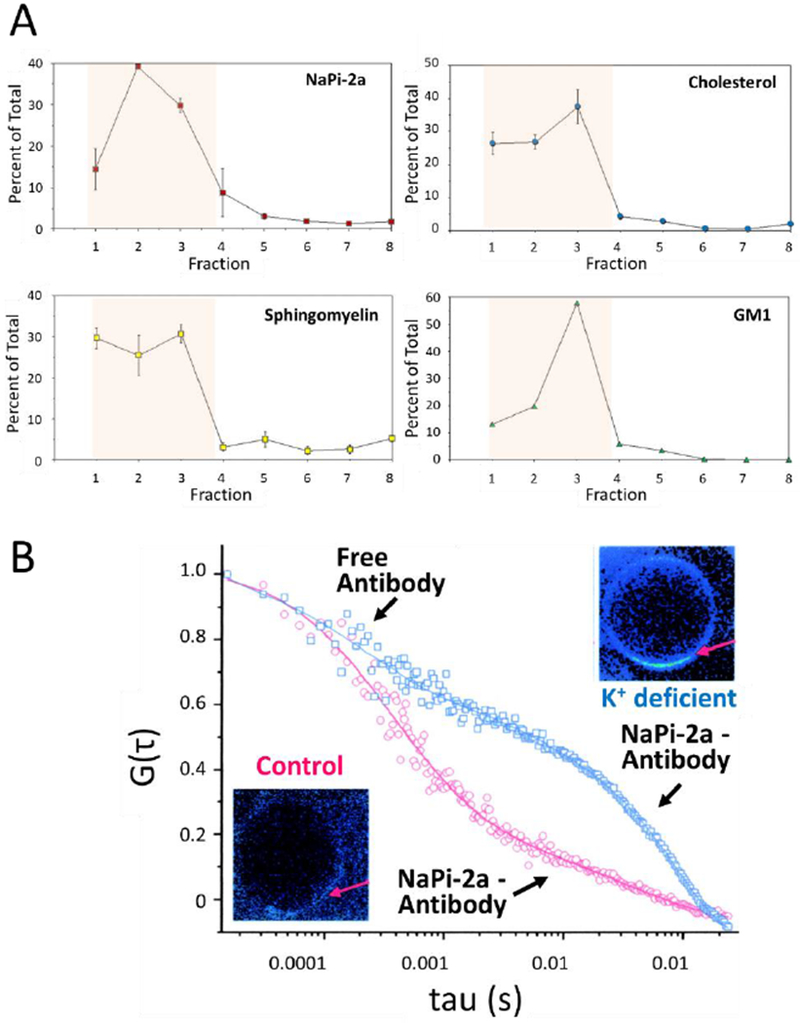
Association of NaPi-2a with lipid rafts. (A) BBM were gradient separated and quantified for NaPi-2a and lipids associated with lipid rafts, cholesterol, sphingomyelin and GM1 (monosialotetrahexosylganglioside) as indicated in the respective panels. NaPi-2a is preferentially partitioned into cholesterol-, sphingomyelin-, and glycosphingolipid-enriched BBM domains, i.e. fractions 1-4 (shaded area). (B) Diffusion of NaPi-2a in giant unilamellar vesicles extracted from K+ deficient (blue squares) and control rats (red squares). In preparations from K+ deficient animals NaPi-2a shows significantly reduced diffusion coefficient as compared to controls. Gt represents the autocorrelation function reflecting fluorescence fluctuation, i.e. fluorophore diffusion; tau represents the time delay. For experimental details see ref 33. The insets are fluorescent representations of giant unilamellar vesicles and the arrow depicts the area that where diffusion was measured. Fluorescence is increased in membranes from K+ deficient animals reflecting an accumulation of transporter at the membrane. Figure adapted from [33].
