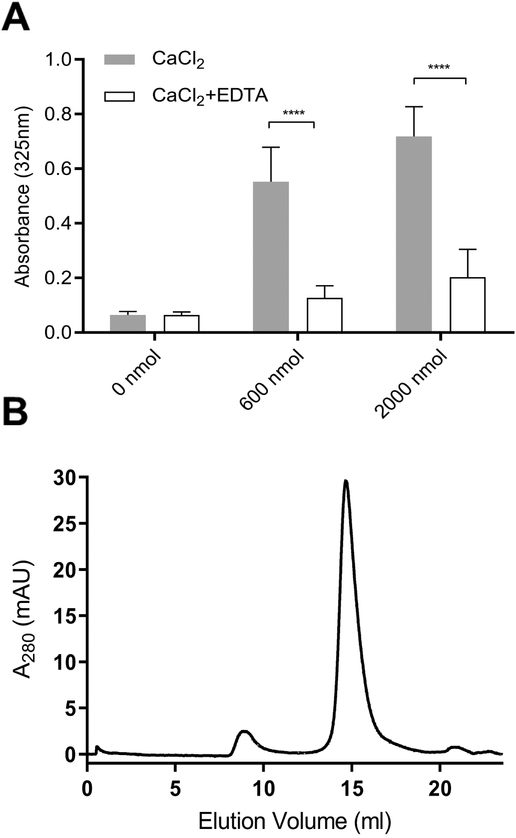
Figure 5. Effect of EDTA on CaCl2-disrupted CL ND.
A) CL ND were formulated in HEPES buffer with apoA-I and aliquots corresponding to 78 nmol CL applied to the wells of a 96 well microtiter plate. Indicated amounts of CaCl2 were added and the volume adjusted to 200 μl with HEPES buffer. The plate was incubated for 1 h at 22 °C and, following incubation, sample absorbance at 325 nm was measured on a Spectramax plate reader. Subsequently, EDTA, dissolved in HEPES buffer, was added to each well to achieve a concentration equivalent to that of the added CaCl2. The final volume of each well was adjusted to 300 μl and the plate incubated for an additional 1 h at 22 °C. Following incubation, sample absorbance at 325 nm was measured. Values reported are the mean ± standard error (n = 6) ****, P<0.0001 calcium-treated versus EDTA-treated. B) FPLC size exclusion chromatography of EDTA-treated, CaCl2-disrupted CL ND. A sample of CL ND (622 nmol CL), solubilized in HEPES buffer, was incubated with 8,000 nmol CaCl2 for 1 h at 22 °C to induce sample turbidity development. To this sample, 8,000 nmol EDTA was added followed by incubation for 1 h at 22 °C to induce sample clarification. The clarified sample was bath sonicated at 48 °C for 2 min followed by chromatography on a Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL FPLC column with elution monitored at 280 nm.