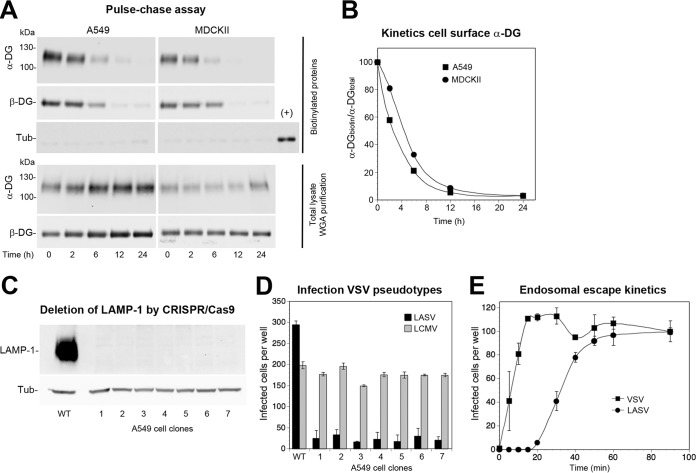
FIG 6.
Steady-state DG uptake and viral entry kinetics. (A) Pulse-chase assay to assess steady-state DG turnover in uninfected cells. Intact monolayers of A549 and MDCKII cells were chilled on ice and subjected to cell surface biotinylation with sulfo-NHS-biotin, followed by reaction quenching in the cold. Cells were washed, prewarmed complete medium was added, and the temperature was shifted to 37°C to restore membrane fluidity. At the indicated time points, cells were chilled on ice, and lysis was performed with cold detergent buffer. Biotinylated proteins were precipitated from 80% of lysates with agarose beads, whereas 20% of lysates underwent WGA purification. As a specificity control for cell surface biotinylation, blots were probed for tubulin in the biotinylated fraction, including 1% of total lysate as a positive control (+). Please note the negligible signal for tubulin in the biotinylated protein fraction, validating the specificity of cell surface labeling. Functional α-DG and β-DG were detected in Western blots as described in the legend to Fig. 1B. One representative example of three independent experiments is shown. (B) Quantification of one out of three representative experiments by densitometry, followed by calculation of the signal ratios of biotinylated α-DG/total α-DG (α-DGbiotin/α-DGtotal). (C) Generation of LAMP-1 null A549 cells. LAMP-1 was deleted from A549 cells by CRISPR/Cas9 as detailed in Materials and Methods and efficiency of depletion was assessed by Western blotting in seven individual clonal LAMP-1 null A549 cell lines using α-tubulin (Tub) as a loading control. (D) DG-dependent rVSVΔG-LASVGP infection of A549 cells depends on LAMP-1. The LAMP-1 null and control A549 cells (C) were infected with rVSV-LASVGP and rVSV-LCMVGP at 300 PFU/well for 1 h. Infection was assessed by direct fluorescence detection of the GFP reporter as described in the legend to Fig. 1D. Data are means plus SD (n = 3). (E) Kinetics of the endosomal escape of virus. rLCMV-LASVGP and rVSV-VSVG at 300 PFU/well were attached to monolayers of the indicated cells in the cold for 2 h in complete medium. Unbound virus was removed, and the cells were rapidly shifted to 37°C. At the indicated time points, 20 mM ammonium chloride was added and left throughout the experiment. After 16 h, infection was assessed by IFA as described in the legend to Fig. 1D. The means ± SD (n = 3) are given. Please note that the half-time of endosomal escape for rLCMV-LASVGP is <40 min. One representative example of three independent experiments is shown.