Fig. 7.
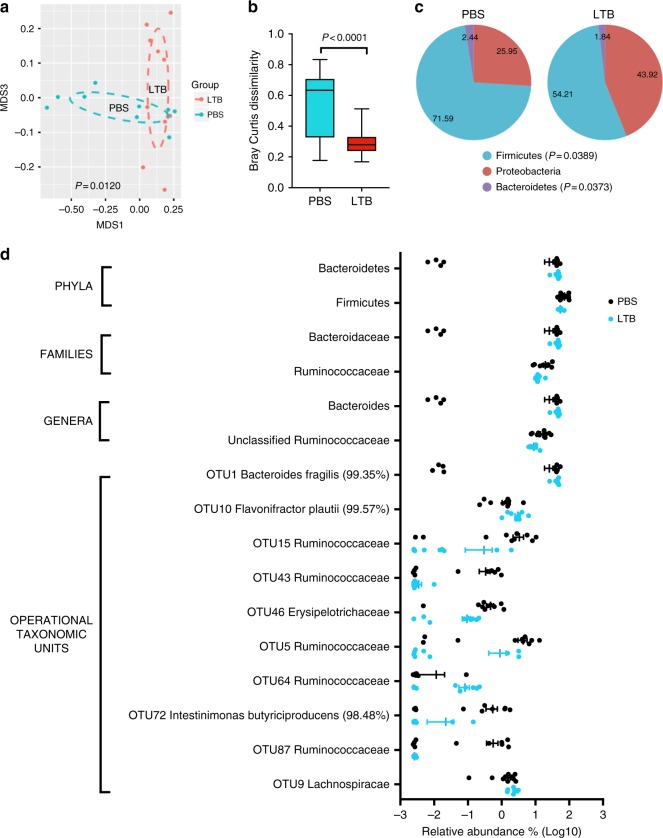
AB5 toxins cause shifts in the gut microbiome of chickens by affecting diversity and composition. a NMDS plot based on Bray Curtis distances show that introduction of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB, n = 9) causes a significant shift (p = 0.0120, Adonis PERMANOVA test) in the gut microbiome of chickens relative to chickens treated with PBS (n = 10). b Although α-diversity is not affected, LTB decreases β-diversity (p < 0.0001, two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction) indicating that the toxin lowers inter-individuality of the gut microbiota. c LTB decreases the relative abundance of Firmicutes (p = 0.0389) with parallel increases in Bacteroidetes (p = 0.0373). d Significant changes in relative abundance (expressed as log10) at selected taxonomic level (see Table 2 for p-values and percentages of relative abundance). Whiskers in b represent minimum and maximum values. Lines and bars in d represent means and standard error of means. Source data are provided as a Source Data file