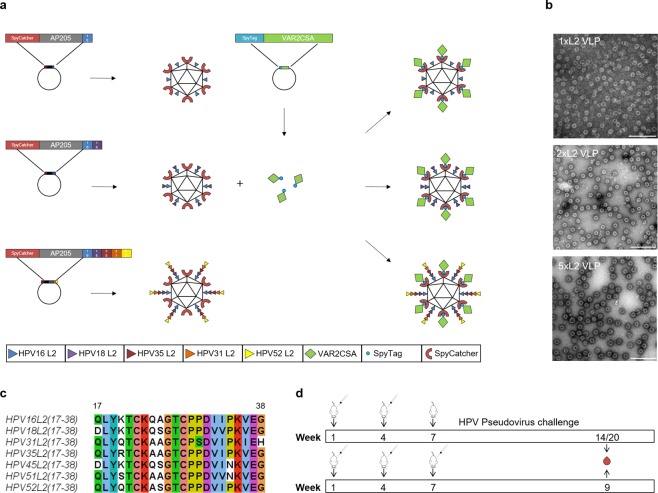
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic representation of the method used to create the combinatorial HPV and PM VLP vaccines. Three combinatorial HPV and PM VLP vaccines were created. Specifically, the AP205 capsid protein was genetically fused to SpyCatcher at the N-terminus whereas the C-terminus was genetically fused to either one (HPV16), two (HPV16 and 18) or five (HPV16, 18, 35, 31, 52) concatenated peptides derived from the highly conserved, cross-reactive epitope of the HPV L2 minor capsid protein (amino acid 17–38). Recombinant expression in E. coli resulted in formation of three distinct VLPs each displaying 180 L2 polypeptides and SpyCatcher proteins. Subsequent mixing of the PM antigen, VAR2CSA (genetically fused to SpyTag at the N-terminus) with VLPs resulted in covalent attachment of VAR2CSA to the surface of the VLPs. (b) Transmission electron microscopy images of the 1xL2-VLP, 2xL2-VLP and 5xL2-VLP. To verify the overall quality of the purified VLPs, the VLP samples were placed on carbon, adsorbed to a grid and negatively stained with 2% uranyl acetate. The three VLPs are non-aggregated and uniform in size (approximately 30–35 nm). Scale bar 200 nm. (c) Amino acid sequence alignment of the minor capsid protein L2 (aa 17–38) from HPV16, 18, 31, 35 and 52. The alignment was created using Jalview36 under a creative commons license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/legalcode). (d) Mouse immunization schedule. Top panel: Balb/C mice were immunized intramuscularly in a prime-boost regimen (week 1 and week 4) with an antigen dose of 5 µg (based on L2-VLP amount) consisting of either 5xL2-VLP (n = 25), 2xL2-VLP (n = 25), 5xL2-VLP-Var2 (n = 6) or 2xL2-VLP-Var2 (n = 6) VLPs. Three weeks following the last immunization, randomized groups of mice (n = 5) were infected vaginally with luciferase-expressing HPV pseudovirions. Blood samples collected at week 14 (for 5xL2-VLP-Var2 and 2xL2-VLP-Var2) or 20 (for 5 × -L2-VLP and 2xL2-VLP) were analyzed for anti-HPV L2 and anti-VAR2CSA IgG antibodies, both with regards to ELISA binding titers as well as in vitro parasite binding-inhibition. Lower panel: Balb/C mice were immunized intramuscularly in a prime-boost-boost regimen (weeks 1, 4 and 7) with a 3.14 µg antigen dose (based on L2-VLP amount) of 1xL2-VLP (n = 7). Blood samples were collected at week 9 to perform ELISA and in vitro PsV challenge.