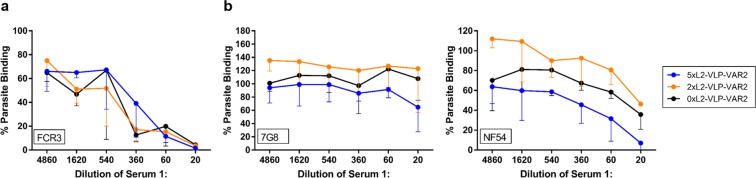
Figure 4.
Functional antibody response against VAR2CSA measured in vitro by a parasite binding-inhibition assay. A static parasite binding-inhibition assay was used to assess the capacity of vaccine-induced mouse antibodies to prevent binding between native VAR2CSA expressed by iE and the human receptor, chondroitin sulfate A (CSA)32,33. In brief, erythrocytes infected with VAR2CSA-expressing tritium-labelled P. falciparum were incubated either without serum (positive control) or with mouse sera in 3-fold dilutions starting at 1:20 in decorin-coated wells. Each assay measured mean iE binding and the percentage of binding iE, by dividing the test result with the mean value of iE in wells incubated without serum. Three repetitions of the assay were made for FCR3 and 7G8 and two for NF54. The graphs show the mean percentage of parasite binding across the technical repetitions of the assay. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of this mean. (a) Normalized iE binding of the homologous FCR3 strain after pre-incubation with different dilutions of pooled mouse sera of mice immunized with either 5xL2-VLP-VAR2CSA (n = 6, blue), 2xL2-VLP-VAR2CSA (n = 6, orange), or 0xL2-VLP-VAR2CSA (n = 5, black. previously published data27 here shown as reference). (b) Normalized iE binding of the heterologous 7G8 strain (left) and NF54 strain (right) after pre-incubation with the indicated dilutions of pooled serum samples as in (a).