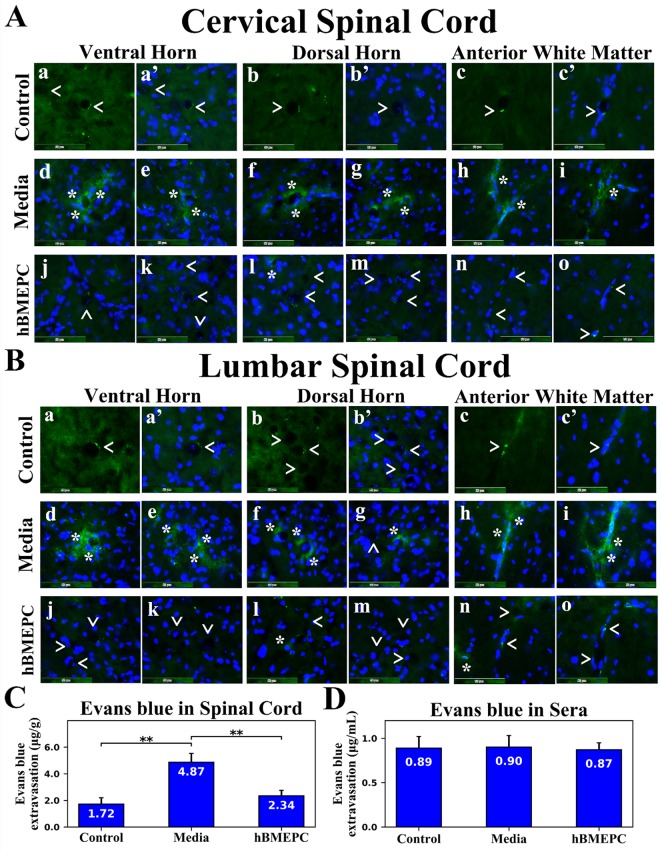
Figure 7.
Characteristics of capillary permeability for Evans Blue in the spinal cords of G93A mice. (A) In the cervical spinal cord, intravenously injected EB was clearly detected within the blood vessels (green, arrowheads) in the ventral horn (a,a’), dorsal horn (b,b’), and anterior white matter (c,c’) from control mice at 17 weeks of age. Vascular leakage (green, asterisks) of EB, even at some distance from capillaries, was observed in the ventral horn (d,e), dorsal horn (f,g), and anterior white matter (h,i) in cervical spinal cords from media-treated animals of the same age. Cell-treated ALS mice showed substantial reductions of leaky capillaries (green, arrowheads) in the ventral horn (j,k), dorsal horn (l,m), and anterior white matter (n,o). Note, a few capillaries leaking EB (asterisk) were detected in the dorsal horn (l) of these animals. The nuclei in a’, b’, c’, d-o are shown with DAPI. Scale bar in a-o is 50 µm. (B) Similar to findings in the cervical spinal cord, EB dye was observed intravascularly (green, arrowheads) in the ventral horn (a,a’), dorsal horn (b,b’), and anterior white matter (c,c’) of the lumbar spinal cords from control mice. Significant diffusion of EB (green, asterisks) into the spinal cord parenchyma from numerous blood vessels was detected in the ventral horn (d,e), dorsal horn (f,g), and anterior white matter (h,i) from media-treated mice. Extensively extravasated EB was determined at a distance from capillaries in the ventral horn (d) and anterior white matter (i). Reduced capillary permeability (green, arrowheads) was shown in the ventral horn (j,k), dorsal horn (l,m), and anterior white matter (n,o) from cell-treated mice. Analogous to the cervical spinal cord, some capillaries showed minor EB leakage (asterisks) in the dorsal horn (l) and anterior white matter (n). The nuclei in a’, b’, c’, d-o are shown with DAPI. Scale bar in A-O’ is 50 µm. (C) Quantitative analysis of EB extravasation into the spinal cord parenchyma demonstrated significantly higher levels of EB in media-treated mice vs. controls. A significant reduction of extravasated EB into the spinal cords was found in ALS mice after cell transplantation. (D) There were no significant differences in EB concentration in sera between control, media, and cell-treated mice. **p < 0.01.