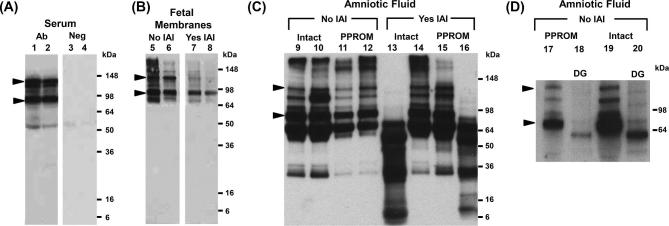
Figure 2.
(A) Representative western blots demonstrating immunoreactive proteoforms of soluble tenascin-X (sTNX) in human serum (lanes 1 and 2) of two women who delivered preterm in the setting of intra-amniotic fluid infection (IAI) and histologic chorioamnionitis. As shown, serum displays TNX immunoreactivity at ∼75 and ∼140 kDa (marked by arrowheads). Negative controls are presented on lanes 3 and 4 where primary antibody was substituted with nonimmune serum. (B) Fetal membranes TNX forms were identified at ∼75 and ∼140 kDa, in a similar fashion to serum and AF (lanes 5–8). (C) Representative western blots of amniotic fluid retrieved from women without (No) or with (Yes) IAI in the setting of either intact or preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM) (lanes 9–16). In the absence of IAI, the characteristic TNX bands at ∼75 and ∼140 kDa were identified. In several AF samples of women with IAI, the characteristic ∼140 kDa sTNX band was absent independent of membrane status (lanes 13 and 16). In these cases, sTNX species of lower molecular weights were identified. (D) Deglycosylation (DG) of two AF samples (lanes 17 and 19) showed that the sTNX proteoforms were glycosylated, given the shift to a lower molecular weight (lanes 18 and 20).