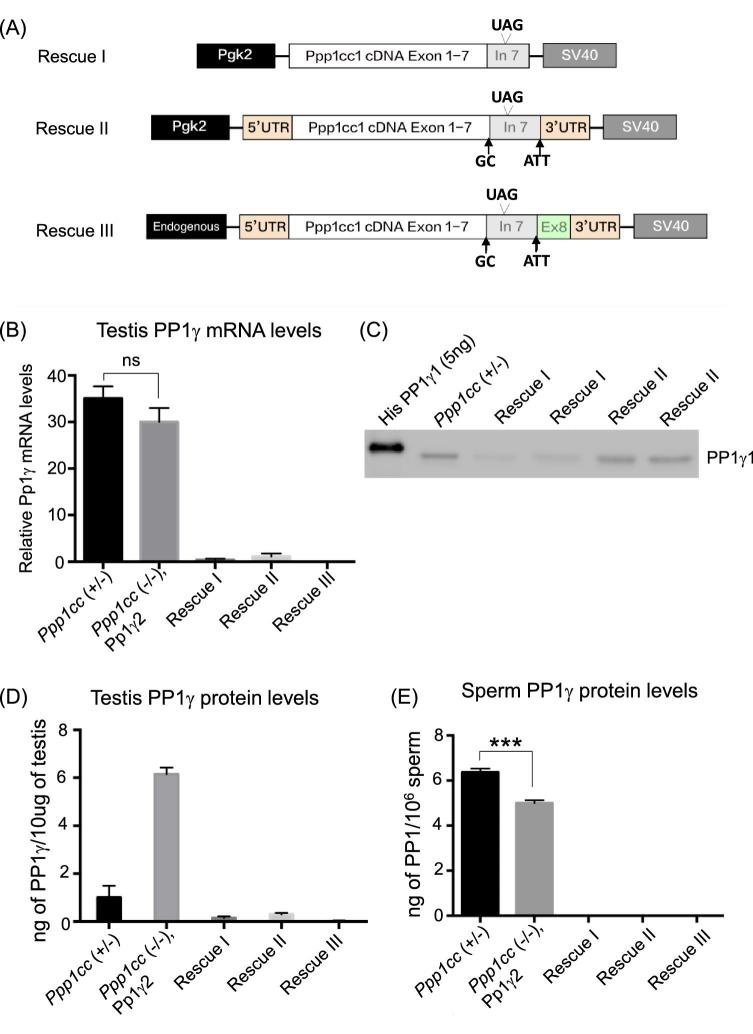
Figure 2.
Design of PP1γ1 Rescue constructs. (A) Driven by the Pgk2 promoter is Rescue I construct consisting of PP1γ1 cDNA including a part of intron 7. Constructs of Rescues II and III contain the entire region of intron 7, as well as the 3΄ and 5΄ UTR's driven by Pgk2 and Ppp1cc endogenous promoters, respectively. The arrows in Rescue II and III indicate mutations of the splice donor and acceptor sites GT to GC and CAG to ATT, respectively. (B) Results of RT-qPCR showing very low levels of PP1γ1 mRNA in testes of Rescue I, Rescue II, and Rescue III in comparison to the heterozygous control “Ppp1cc (+/–)” and the PP1γ2 rescue “Ppp1cc (–/–), Pp1γ2”. (C) Western blot analysis of testis extracts along with 5 ng of His-PP1γ1 recombinant protein probed with anti-PP1γ1 antibody. (D) Quantification of the levels of PP1γ1 protein in testis of Ppp1cc (+/–) and rescue I, II, and III in comparison to PP1γ2 of Ppp1cc (–/–), Pp1γ2” estimated by the immunoreactivity intensity comparison with known amounts of recombinant PP1γ1/γ2 protein in western blot analysis from six blots. (E) Levels of PP1γ1 protein incorporated in 2 × 106 sperm based on comparison with recombinant PP1γ1 protein (western blot not shown). All error bars represent the standard error of the mean SEM. ***P < 0.001, n.s indicates not significant.