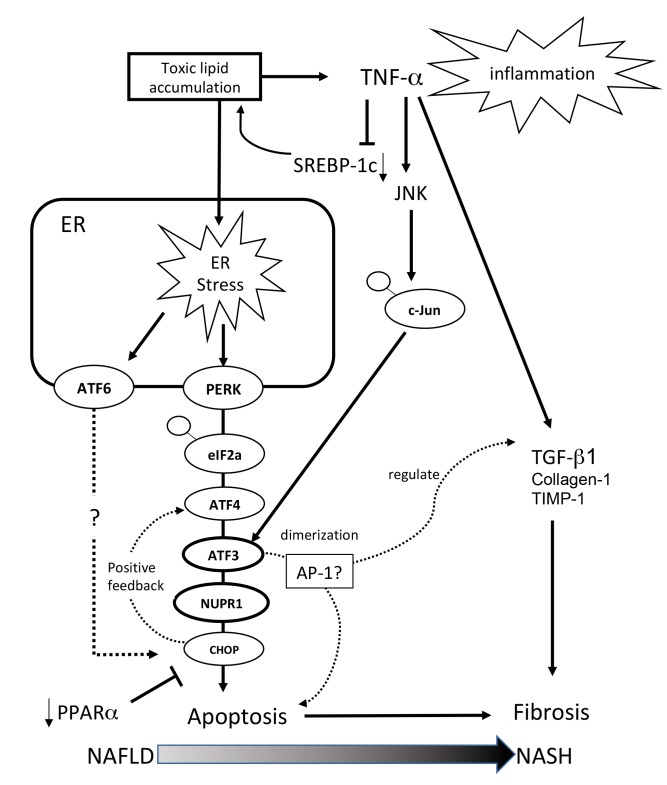
Fig. 6.
Schematic of gene expression around the ATF3/NUPR1 axis. Excess toxic lipid induces inflammation through TNF-α, excessive ER stress is transduced through the ATF3 and NUPR-1 axis, and the excessive ER stress response ameliorates the protective effect of PPAR-α. For this reason, apoptosis and accelerated fibrosis are evident in the NASH mouse model. AP-1, activator protein-1; ATF, activating transcription factor; Chop, C/EBP homologous protein; c-Jun, jun proto-oncogene; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; JNK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NUPR-1, nuclear protein-1; PERK, pancreatic ER kinase; PPAR-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha; SREBP, sterol regulatory element binding protein; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.