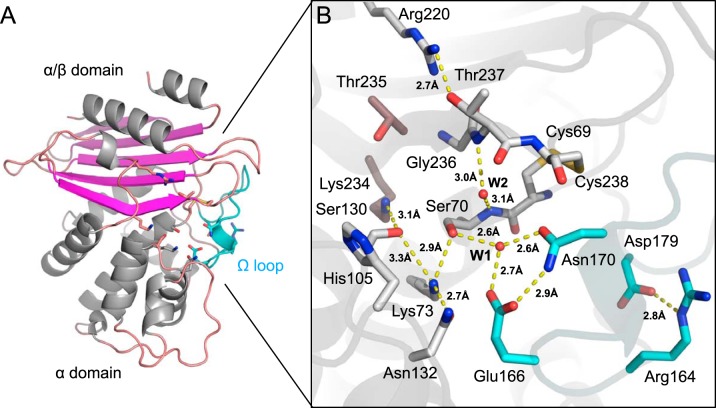
FIG 3.
X-ray structure of native VCC-1. (A) VCC-1 adopts a two-domain fold typical of other class A enzymes; one has an α/β topology, whereas the other is α helical. Residues comprising the active site are located at the interface of the two domains and shown as sticks. The omega loop containing the catalytic general base Glu166 is colored cyan. (B) Close-up of the VCC-1 active site. The hydrogen-bonding network and water content are consistent with β-lactam acylation occurring via an energetically favorable proton transfer from Lys73 to Glu166 via Ser70 and active-site water W1 (32). Only the dominant His105 side chain conformation is shown.