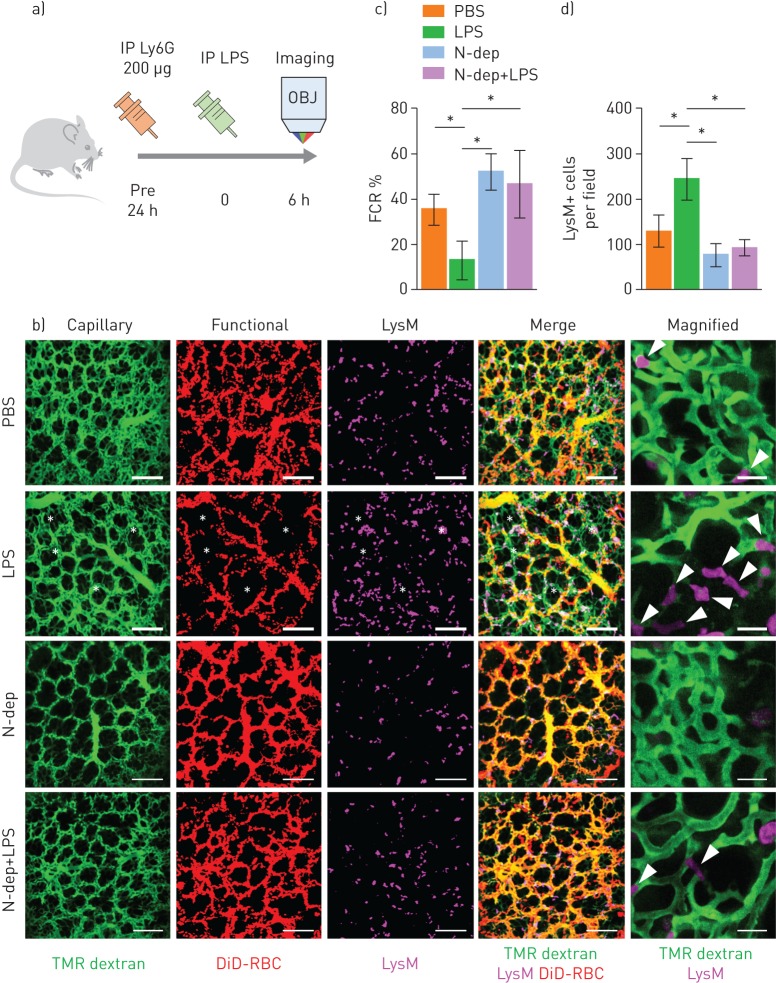
FIGURE 5.
Neutrophil depletion (N-dep) improves the functional capillary ratio (FCR) of the pulmonary microcirculation in a sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) model. a) Schematics of intravital lung imaging of N-dep in a sepsis-induced ALI model. b) Representative intravital imaging of FCR in the pulmonary microcirculation in the PBS, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), N-dep and N-dep+LPS group. Anatomical capillary (tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) dextran, green), functional capillary (DiD-labelled erythrocyte, red) and LysM+ (LysMGFP/+, magenta) cell imaging was acquired. White asterisks indicate dead spaces. Magnified images show entrapped LysM+ cells (arrowheads) and consequent flow disturbance (supplementary video S9). Scale bars, 20 µm in magnified, otherwise, 100 µm. c, d) Comparisons of FCR (%) and LysM+ cell count among PBS, LPS, N-dep and N-dep+LPS groups (n=30, 10 fields of view per mouse, three mice per group, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Holm–Sidak's multiple comparisons test, *p<0.05). Data are presented as mean±sd. IP: intraperitoneal; OBJ: objective lens; RBC: red blood cells.