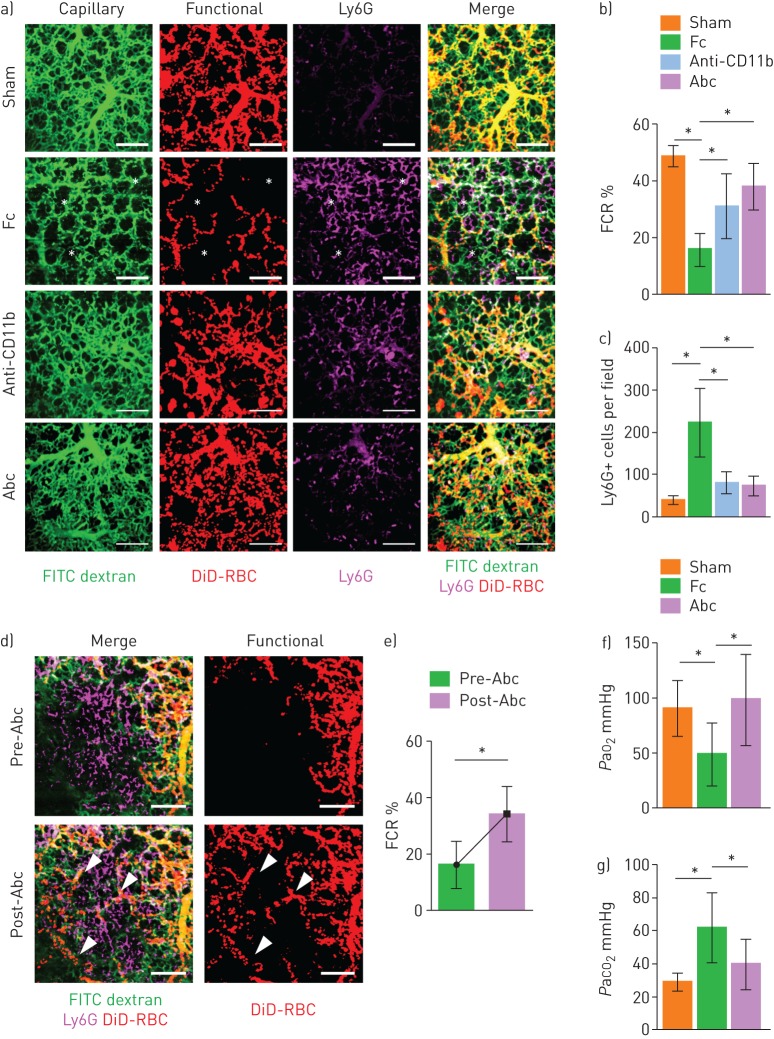
FIGURE 7.
Mac-1 inhibitor ameliorates the functional capillary ratio (FCR) of the pulmonary microcirculation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. a) Representative intravital imaging of FCR in the pulmonary microcirculation in the sham, fragment crystallisable (Fc), Anti-CD11b and abciximab (Abc) groups. Anatomical capillary (tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) dextran, green), functional capillary (DiD-labelled erythrocytes, red) and neutrophil (Ly6G, magenta) imaging was acquired. White asterisks indicate dead spaces. Scale bars, 100 µm. b, c) Comparisons of FCR and number of Ly6G+ cells in the pulmonary microcirculation (n=14–25, three mice per group, two-tailed t-test, *p<0.05). Data are presented as mean±sd. d) Representative intravital lung imaging of the pre- and post-Abc groups (supplementary video S10). White arrowheads indicate restoration of erythrocyte perfusion. Scale bars, 100 µm. e) Comparison of FCR in the pre- and post-Abc groups (n=20 and 24, 6–8 fields of view per mouse, three mice per group, two-tailed t-test, *p<0.05). Data are presented as mean±sd. f, g) Comparisons of the arterial oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2) tension in the sham (n=8), Fc (n=10) and Abc (n=6) groups (Kruskal–Wallis test with post hoc Dunn's multiple comparison tests, *p<0.05). Data are presented as mean±sd. RBC: red blood cells.