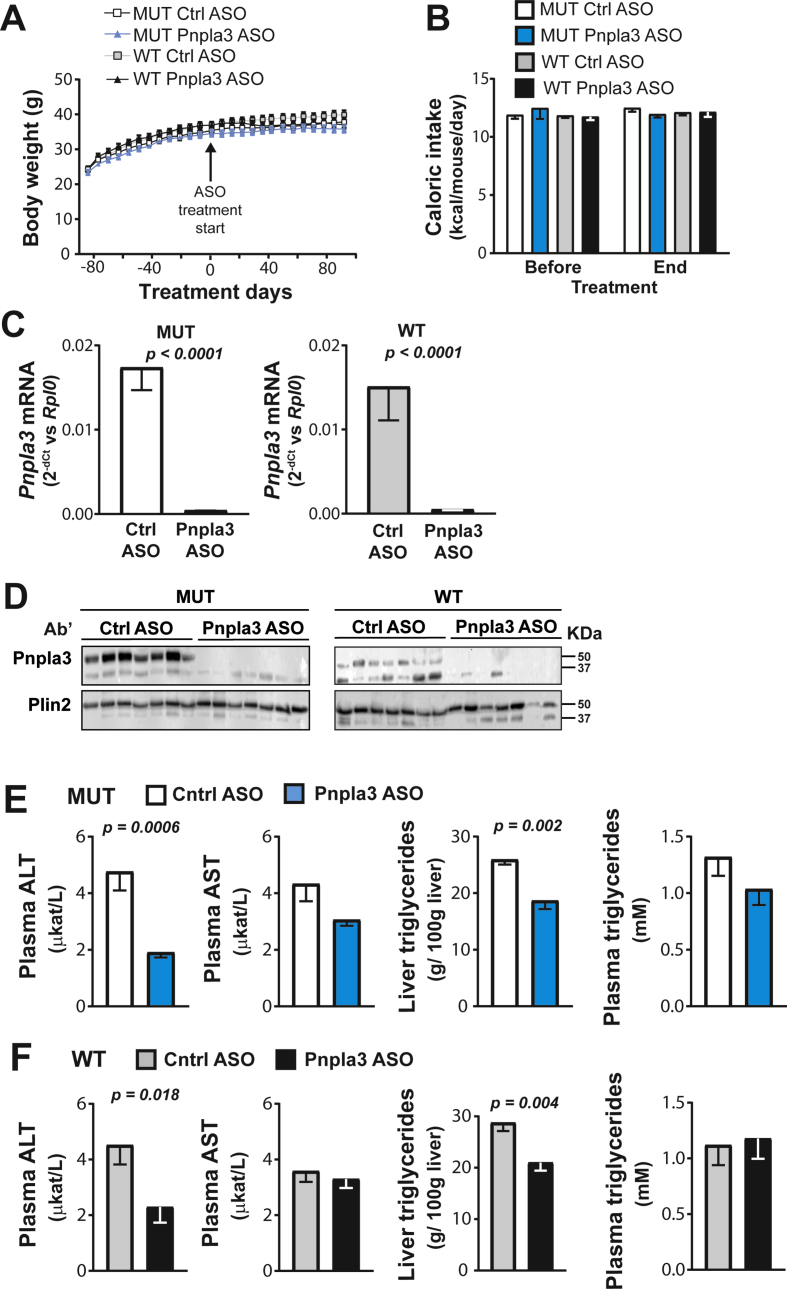
Figure 2.
The Pnpla3 ASO treatment reduced liver Pnpla3 mRNA and protein levels and liver triglyceride levels in both Pnpla3 mutant knock-in mice and wild-type littermates fed a NASH-inducing diet. A total of 17 male homozygous Pnpla3 148M/M (mutant) knock-in mice and 17 wild-type littermates were fed a NASH-inducing diet for 26 weeks. After 12 weeks of consumption of the NASH diet, mice were assigned to ASO study groups based on body weight. Pnpla3 mutant knock-in and wild-type mice were treated with either control or Pnpla3 ASOs (5 mg/kg/week administered by two subcutaneous injections per week, n = 8–9 mice/group) for 14 weeks. (A) Body weight was measured throughout the experiment, while (B) caloric intake was measured before and after the ASO treatment. (C) Liver Pnpla3 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR and normalized to Rplp0. (D) Levels of the Pnpla3 protein in hepatic lipid droplets were measured by western blotting. Plin2 was used as the loading control. Hepatic lipid droplets were purified by density gradient ultracentrifugation (see the Materials and Methods). Plasma ALT, AST, and triglyceride levels and the liver triglyceride content in the Pnpla3 mutant knock-in (F,G) and wild-type (I,J) mice were measured using biochemical assays. Values are presented as the mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using 2-sided t-tests. Abbreviations: ASO: antisense oligonucleotide; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; Plin2: perilipin 2; Pnpla3: patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3; Rplp0: ribosomal protein large P0; Ctrl: control; AU: arbitrary unit. Mutant knock-in mice are defined as homozygotes for a methionine (M) at position 148 of the Pnpla3 protein, while wild-type littermates are homozygotes for an isoleucine (I) at the same position. WT: wild-type; MUT: mutant.