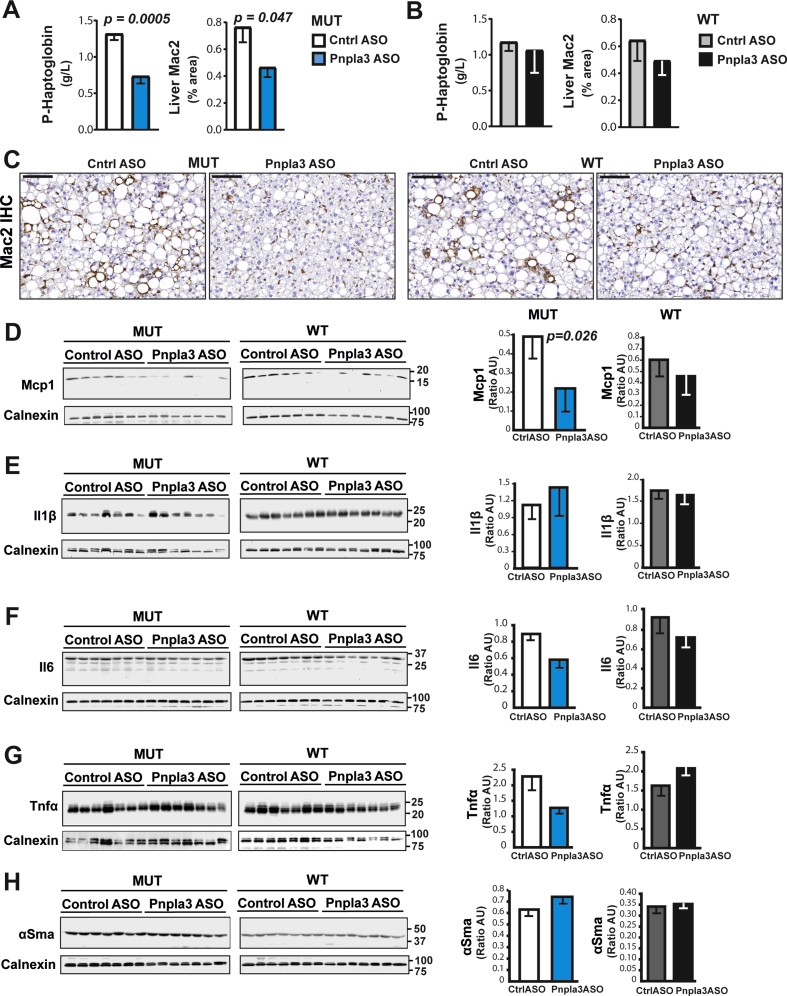
Figure 5.
The Pnpla3 ASO treatment reduced plasma haptoglobin levels, liver macrophage content, and Mcp1 levels in Pnpla3 mutant knock-in mice fed a NASH-inducing diet. Homozygous Pnpla3 mutant knock-in and wild-type littermates were fed a NASH-inducing diet for 26 weeks. After 12 weeks of consuming the NASH diet, Pnpla3 mutant knock-in and wild-type mice were treated with either control or Pnpla3 ASOs (5 mg/kg/week administered by two subcutaneous injections per week, n = 8–9 mice/group) for 14 weeks. Plasma haptoglobin levels and liver macrophage contents (as determined by Mac2 staining) in Pnpla3 mutant knock-in (A) and wild-type (B) mice. (C) Representative images of Mac2-stained liver sections (black scale bar represents 100 μm). Liver protein levels of Mcp1 (D), Il1β (E), Il6 (F), Tnfα (G), and αSma (H) measured with western blot analyses. Values are presented as the mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using 2-sided t-tests. Abbreviations: αSma: alpha-smooth muscle actin; ASO: antisense oligonucleotide; Ctrl: control; Il: Interleukin; Mac2: macrophage antigen 2. Mcp1: monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; Pnpla3: patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3; Tnfα: tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mutant knock-in mice are defined as homozygotes for a methionine (M) at position 148 of the Pnpla3 protein, while wild-type littermates are homozygotes for an isoleucine (I) at the same position. WT: wild-type; MUT: mutant.