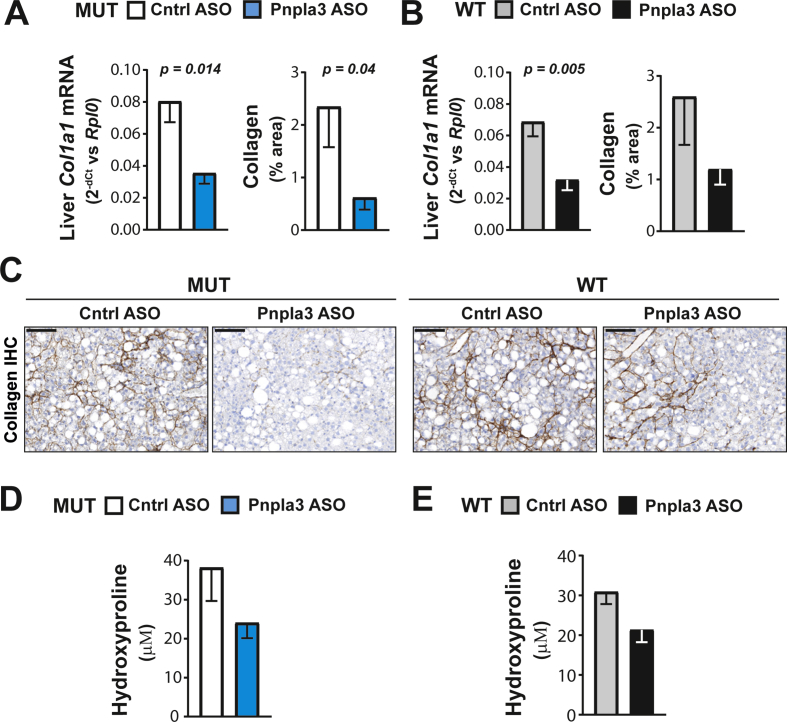
Figure 6.
The Pnpla3 ASO treatment reduced liver fibrosis in Pnpla3 mutant knock-in mice fed a NASH-inducing diet. Homozygous Pnpla3 mutant knock-in and wild-type littermates were fed a NASH-inducing diet for 26 weeks. After 12 weeks of feeding on the NASH diet, Pnpla3 mutant knock-in and wild-type mice were treated with either control or Pnpla3 ASOs (5 mg/kg/week administered by two subcutaneous injections per week, n = 8–9 mice/group) for 14 weeks. Liver Col1a1 mRNA and protein (immunohistochemistry) levels in Pnpla3 mutant knock-in (A) and wild-type mice (B). (C) Representative images of collagen immunohistochemistry in liver sections (black scale bar represents 100 μm). Liver hydroxyproline levels in Pnpla3 mutant knock-in (D) and wild-type mice (E). Values are presented as the mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using 2-sided t-tests. Abbreviations: ASO: antisense oligonucleotide; Col1a1: collagen type I alpha 1 chain; Ctrl: control; Rplp0: ribosomal protein large P0. Mutant knock-in mice are defined as homozygotes for a methionine (M) at position 148 of the Pnpla3 protein, while wild-type littermates are homozygotes for an isoleucine (I) at the same position. WT: wild-type; MUT: mutant.