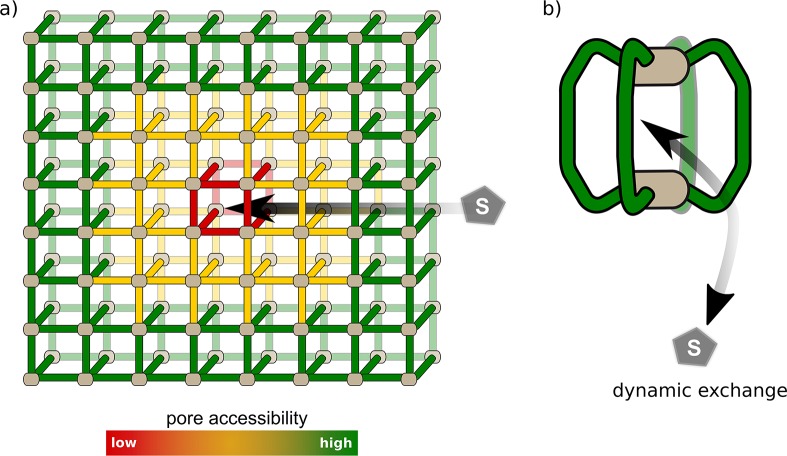
Figure 5.
Comparison of pore accessibility. (a) In MOFs, accessibility is dependent on grain size, pore window size, and diffusion within the MOF crystal. Pores deeply buried inside the crystal (red) are less accessible. Thus, incorporated functionalities in these positions are less likely to contribute to the overall activity of the material. (b) MOCs possess only a few pores, and accessibility depends only on host–guest and solvent interactions. Exchange of guests (e.g., anions, small molecules) is often a very dynamic process. MOCs can be viewed as the smallest possible MOF-like assemblies.