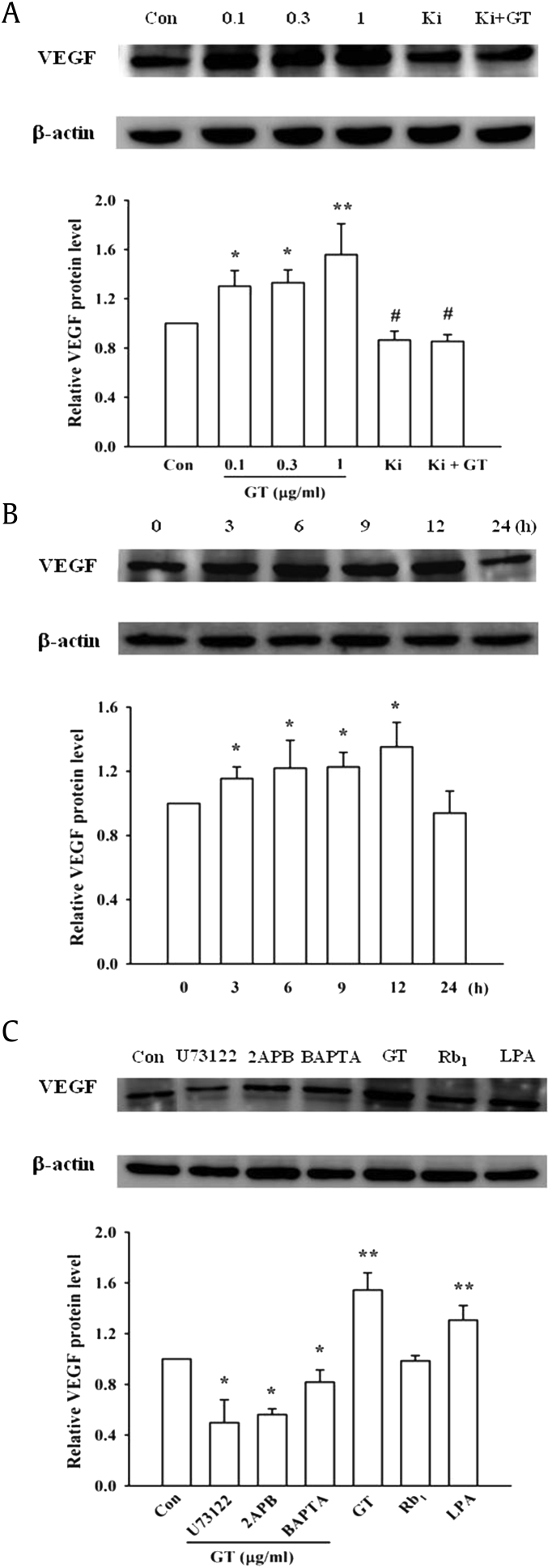
Fig. 2.
Western blots showing the expression of VEGF in extracts of primary astrocyte cultures following treatment with gintonin (GT) or inhibitors of signal transduction. (A) The expression of VEGF protein in primary astrocytes following treatment with various concentrations of GT or in the presence of Ki16425 (10 μM). Histograms indicating the levels of VEGF protein expressed in the astrocytes, which were quantified by their density in western blotting experiments. (B) Time course of VEGF protein expression in primary astrocytes treated with 1 μg/mL GT. (C) GT-mediated VEGF protein expression in cells treated with inhibitors of the signal transduction pathway. The concentrations of the inhibitors were the same as those in Fig. 1C. ∗p < 0.01, compared to the control (Con); #p < 0.05, compared to treatment with 1 μg/mL GT. All the data were normalized to the levels of the β-actin protein. The data are represented as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3–4). **p < 0.001, compared to the control (Con).
LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; S.E.M., standard error of the mean; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.