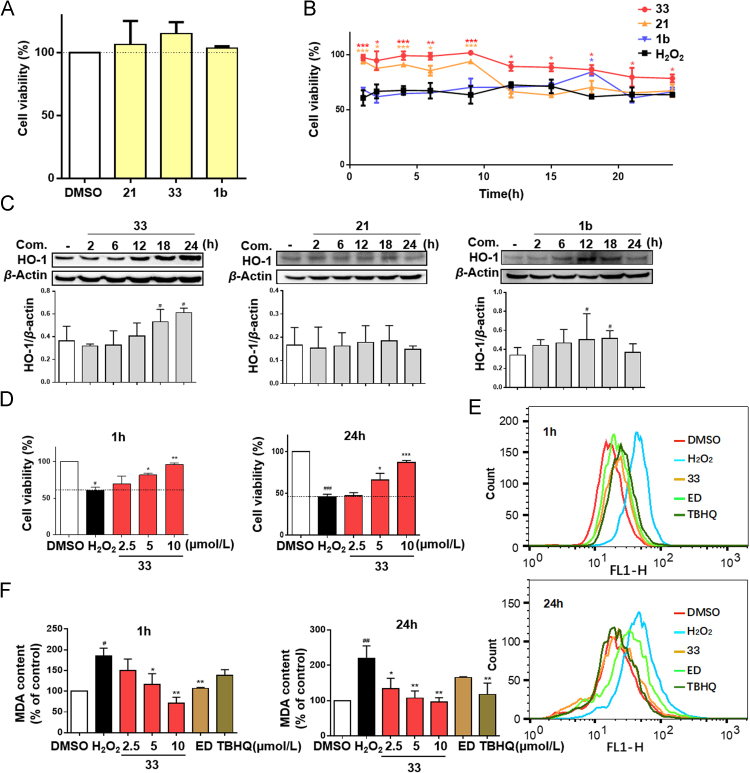
Figure 2.
The cytoprotective effects of 33 on PC12 cells subjected to H2O2. (A) Cytotoxicity screening of 33 in PC12 cells. The cells were treated with 10 μmol/L of 21, 33 and 1b for 24 h, and the cytotoxicity of compounds were determined by the MTT assay. (B) Protection of compound 33 against H2O2-induced PC12 cell damage. PC12 cells were incubated with 10 μmol/L of 33, 21, 1b for 1, 2, 4, 6, 9,12, 15, 18, 21 and 24 h before exposed to H2O2 (450 μmol/L) for additional 24 h. Then the cell viability was determined by MTT assay. (C) Elevating the expression level of protein HO-1 by 33. PC12 cells were incubated with 33 (10 μmol/L), 21(10 μmol/L), 1b (10 μmol/L) for 2, 6, 12,18 and 24 h, and the HO-1 was determined by Western blot experiment. (D) 33 protected PC12 cells from H2O2-induced cell injury. PC12 cells were pretreated with 33 in different doses (2.5, 5 and 10 μmol/L) for 1 or 24 h, then treated with 450 μmol/L H2O2 for 24 h, and determined by the MTT assay. (E) 33 decreased ROS level in H2O2-treated PC12 cells. PC12 cells were pre-treated with 10 μmol/L of 33, ED or TBHQ, then treated with H2O2 for 4 h, and the ROS level was measured by flow cytometry. (F) Protection of compound 33 by reducing MDA. PC12 cells were pre-incubated with 33 at 2.5, 5 and 10 μmol/L, ED (10 μmol/L) or TBHQ (10 μmol/L) for 1 or 24 h, then treated with 700 μmol/L H2O2 for 16 h, finally determined by the manufacturer׳s instructions. Data are expressed as the mean±SD (n=3). ###P<0.001, ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 significantly different from control group, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 significantly different from H2O2 group.