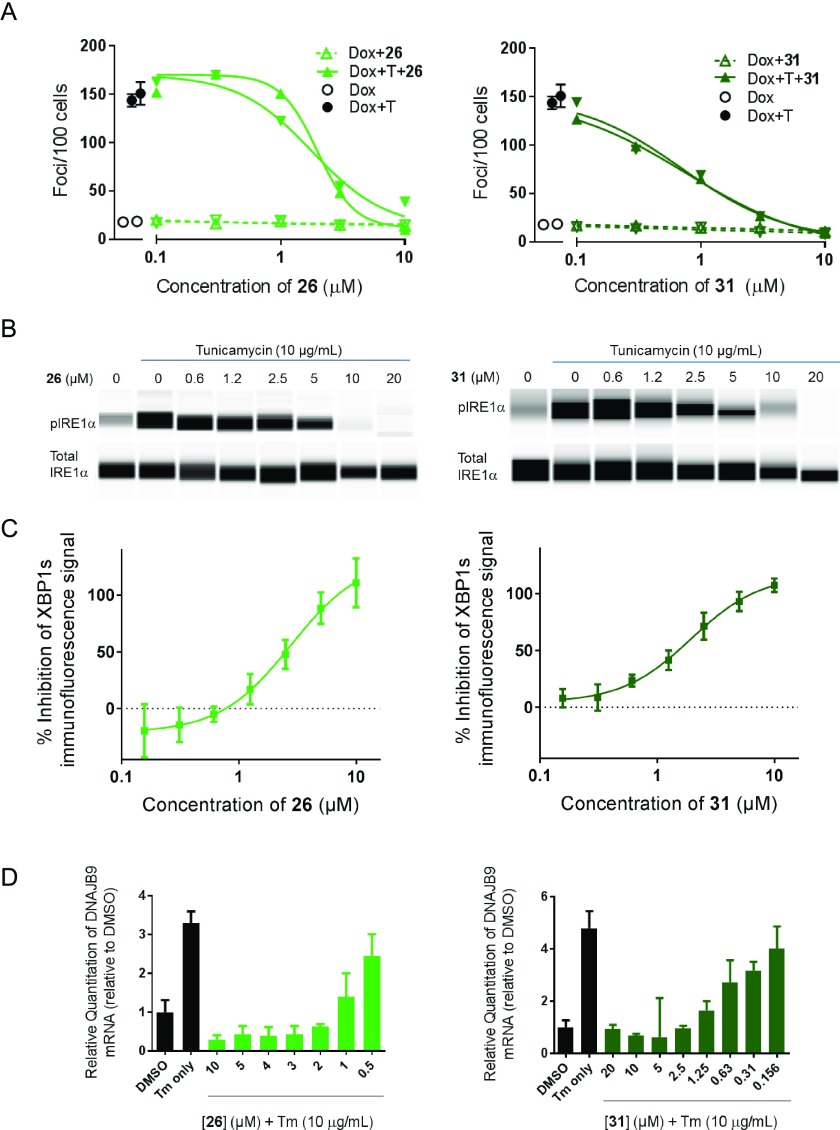
Figure 4.
Compounds 26 and 31 inhibit IRE1α oligomerization, IRE1α autophosphorylation, IRE1α RNase activity, XBP1s protein expression, and XBP1-dependent transcription in human cells. (A) Inhibition of tunicamycin-induced IRE1α oligomerization, measured by fluorescent foci formation in HEK293 cells stably transfected with doxycycline-inducible GFP-IRE1α after 5 h treatment with inhibitors (0–10 μM) in the absence or presence of tunicamycin (quantification of image fields from n = 2 experiments plotted separately). Dox = doxycycline, T = tunicamycin (10 μg/mL). (B) Inhibition of tunicamycin-induced pS724 IRE1α autophosphorylation as measured by capillary electrophoresis immunoassay (simple Western) relative to total IRE1α. Data shown for a single experiment representative of n = 3. (C) Inhibition of tunicamycin-induced XBP1s protein expression in H929 cells as measured by immunofluorescent assay (quantification of image fields from n > 3 experiments). (D) Inhibition of tunicamycin-induced XBP1s-dependent transcription of DNAJB9 mRNA as measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Data shown for a single experiment representative of n = 3. Tm = tunicamycin.