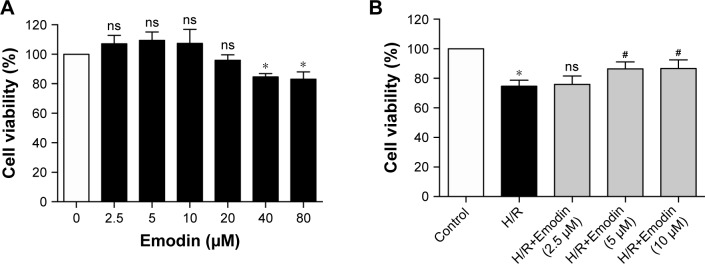
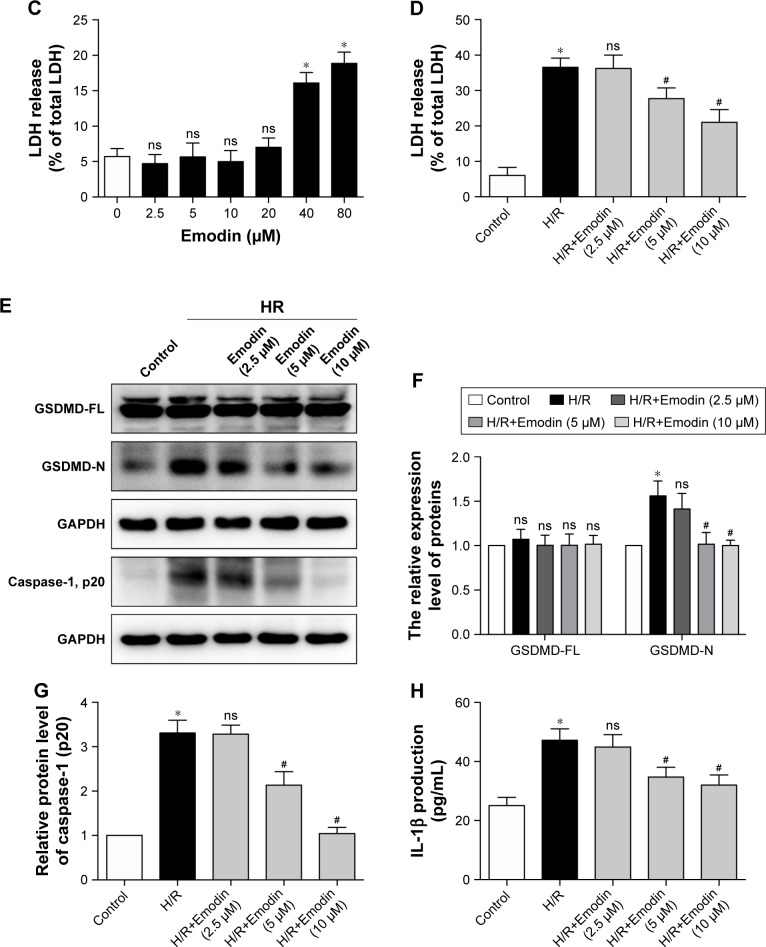
Figure 3.
Emodin protected cardiomyocytes from H/R-induced pyroptosis.
Notes: (A) Cell viability was assessed by using the CCK-8 assay. Primary cardiomyocytes were incubated in a medium with emodin at 0–80 µM for 1 hour, and cells without emodin treatment were defined as the control and were considered to have 100% cell viability. (B) Primary cardiomyocytes were treated with H/R or H/R plus emodin. Cell viability was assessed by using CCK-8 assays. Cells under normoxic conditions were defined as the control and considered to have 100% cell viability. (C) Percentage of LDH release in cell culture supernatants with emodin at 0–80 µM for 1 hour. (D) Percentage of LDH release in cell culture supernatants among control, H/R, and H/R plus emodin groups. (E) Representative Western blot luminogram of GSDMD-FL, GSDMD-N, and caspase-1 (p20) in the primary cardiomyocytes. (F) Protein semiquantification is shown for GSDMD-FL and GSDMD-N based on the results of 3E. (G) Protein semiquantification is shown for caspase-1 (p20) based on the results of 3E. (H) Concentrations of IL-1β in cell culture supernatants were detected by ELISA. The protein level was standardized by GAPDH. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05 vs the control group, #P<0.05 vs the H/R group. Abbreviations: CCK, Cell Counting Kit; H/R, hypoxia/reoxygenation; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; GSDMD-FL, gasdermin D-full length; ns, not significant.