Fig. 3.
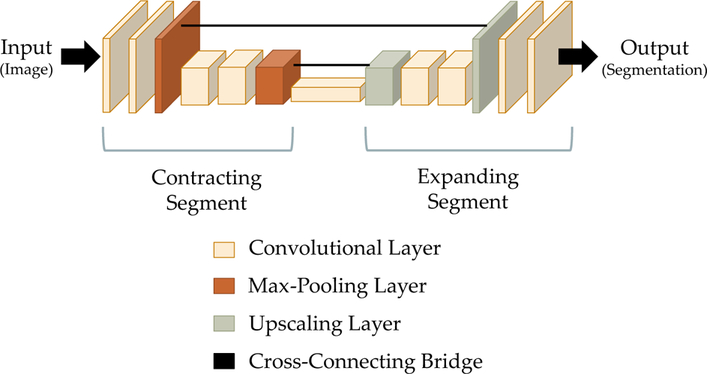
A schematic diagram of the U-Net architecture, a fully convolutional neural network that is often used for the semantic segmentation of biomedical images [18]. The architecture consists of a contracting segment (left), in which convolutional layers are followed by max pooling layers that downscale the image, followed by a expanding segment (right), in which convolutional layers are intermixed with upscaling layers that increase the size of the image. Cross-connecting bridges (center) connect corresponding layers in the contracting and expanding segments. These bridges preserve detailed information that would otherwise be lost during the max pooling operations. The height and width of each block in the block diagram reflect the height and width of the image as it is encoded at that point. The thickness reflects the number of feature channels
