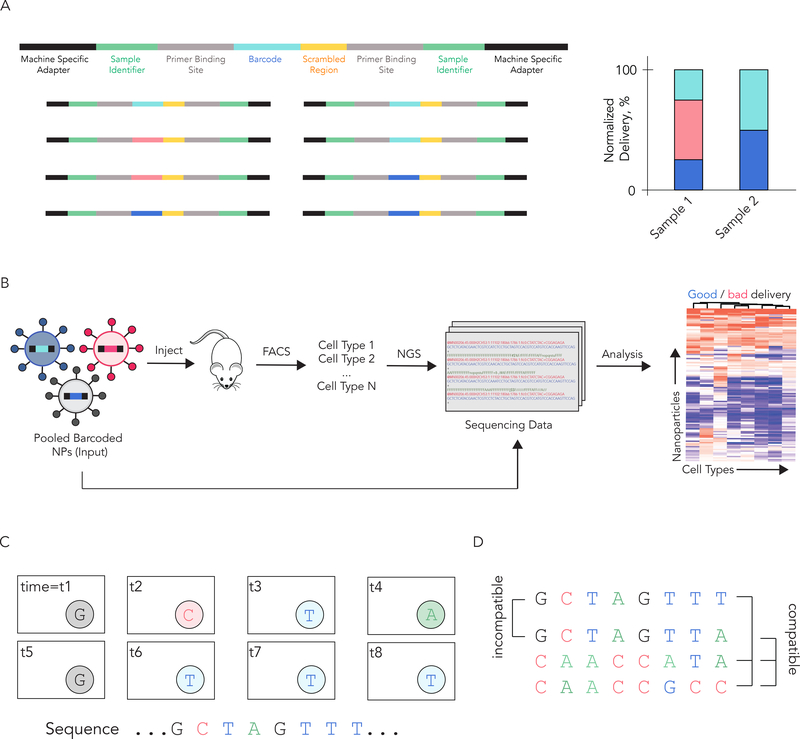
Figure 3.
DNA barcodes can be rationally designed to track hundreds of nanoparticles in vivo using next generation sequencing. (A) JORDAN barcodes contain universal primer sites, a 7 nucleotide randomized region, and an 8 nucleotide barcode region. This barcode design allows us to multiplex hundreds of different barcodes. The normalized delivery for every barcoded LNP is determined; this is analogous to ‘counts per million’ in RNAseq studies. (B) JORDAN uses DNA barcodes and next generation sequencing to analyze the biodistribution of thousands of particles in vivo. Next generation sequencing is an effective way to read DNA barcodes. (C) Solid phase next generation sequencing reads each nucleotide of the sequencing using fluorescent nucleotides. Understanding how NGS generates data is important to understanding barcode design; NGS is reviewed extensively in reference 47. (D) For example, it is helpful if the sequence of a barcode differs from all other barcodes at 3 of the 8 positions.