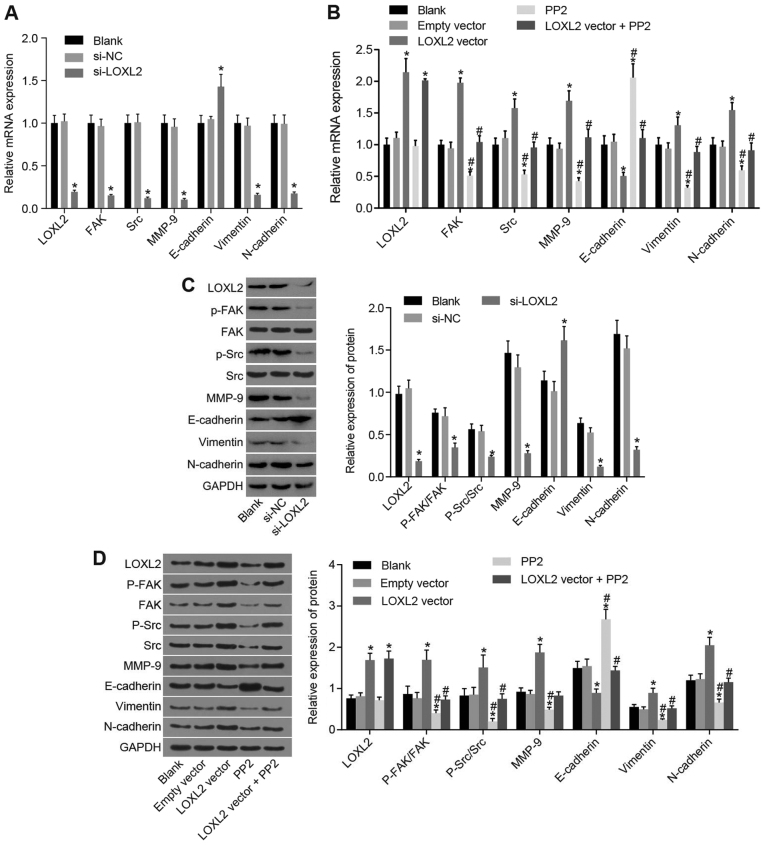
Figure 6.
Silencing of LOXL2 inhibited activation of the FAK/Src pathway and affected factors associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. (A) Once 786-O cells were transfected with si-LOXL2, the mRNA expression of FAK, Src, MMP-9, N-cadherin and vimentin were significantly decreased and that of E-cadherin was significantly increased; *P<0.05 vs. blank and si-NC groups. (B) Once Caki1 cells were transfected with the LOXL2 vector, the mRNA expression of FAK, Src, MMP-9, N-cadherin and vimentin were significantly increased and that of E-cadherin was significantly decreased. In the PP2 group, mRNA expression changes exhibited the opposite trend. *P<0.05 vs. the blank and empty vector groups; #P<0.05 vs. the LOXL2 vector group. (C) Once 786-O cells were transfected with si-LOXL2, the protein expression of FAK, Src, MMP-9, N-cadherin and vimentin was significantly decreased and that of E-cadherin was significantly increased. *P<0.05 compared with the blank and si-NC groups. (D) Once Caki1 cells were transfected with LOXL2 vector, the protein expressions of FAK, Src, MMP-9, N-cadherin and vimentin were significantly increased and that of E-cadherin was significantly decreased. In the PP2 group, protein expression changes exhibited the opposite trend. *P<0.05 vs. the blank and empty vector groups; #P<0.05 vs. the LOXL2 vector group. One-way analysis of variance was used for comparison and the experiment was repeated three times. LOXL2, lysyl oxidase-like 2; Src, steroid receptor coactivator; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NC, negative control; P-, phosphorylated; si-, small interfering RNA; N-cadherin, neuronal cadherin; E-cadherin, epithelial cadherin.