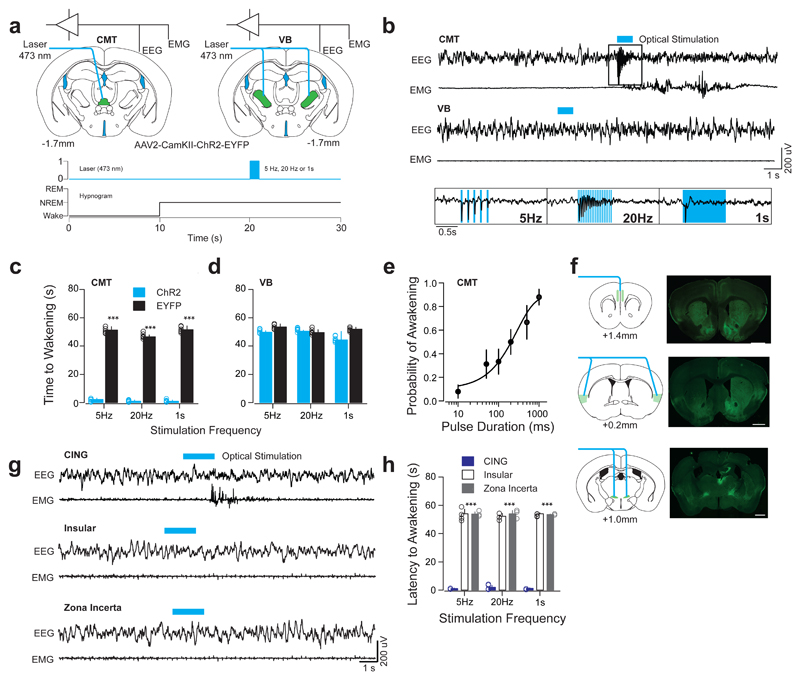
Figure 3. Optogenetic activation of CMT, but not VB, neurons entrains cortical UP-like states and induces arousal.
a, Schematic of a brain coronal section illustrating the AAV2-CamKII-ChR2-EYFP or AAV2-CamKII-EYFP (control) injection sites and chronic optical fiber implantation in CMT (left) and VB (right) areas. Bottom, experimental timeline showing blue optical stimulation trains (blue bar) delivered 10 s after the onset of NREM. b, Representative EEG/EMG traces from CMT (top) and VB (middle) illustrate arousal responses upon optogenetic activation. Note the high-fidelity entrainment of cortical activity upon optical activation of ChR2-EYFP-expressing CMT neurons at 5 and 20 Hz or continuous illumination (1 s, blue bar; bottom insets). c, d, Averaged latencies to awakening ± S.E.M. following optogenetic CMT (c) or VB (d) neuron activation (n = 6 animals per group). Data is based on a minimum of 10 stimulations per frequency per animal. (5 Hz: P = 0.00008; t = 26.75; d.f. = 10; 20 Hz: P = 0.00006; t = 41.68; d.f. = 10; 1 s: P = 0.00006; t = 27.23; d.f. = 10; two-sided t-test). e, Averaged probability of awakenings ± S.E.M. upon increasing durations of single-pulse optogenetic CMT neuron activation. Values represent (Boltzmann sigmoidal curve fit, based on a minimum of 10 stimulations per duration per animal). f, Schematic for optogenetic activation of CMT axon terminals (left panels) and representative photomicrographs of coronal brain sections showing of ChR2-EYFP-expressing CMT axons (right panels) in CING (top), insular cortex (middle) and ZI (bottom). Scale bar: 1 mm. g, Representative EEG/EMG traces illustrate arousal response upon optogenetic activation of ChR2-EYFP-expressing CMT axons in CING (top), insular cortex (middle) and ZI (bottom) at various frequencies (5Hz, 20Hz, or continuous, 1 s; blue bar). Note the absence of awakenings upon activation of insular cortex or ZI. h, Averaged latencies to awakening ± S.E.M. upon optical activation of ChR2-EYFP-expressing CMT axon terminals in CING, insular cortex and ZI (minimum of 10 stimulations per frequency per animal, n = 5 animals per group). Note that stimulation of CING in non-transfected control animals did not induce awakening (P = 0.00013; f = 2567; d.f. = 2; two-way ANOVA).