Fig. 2:|. B cell development.
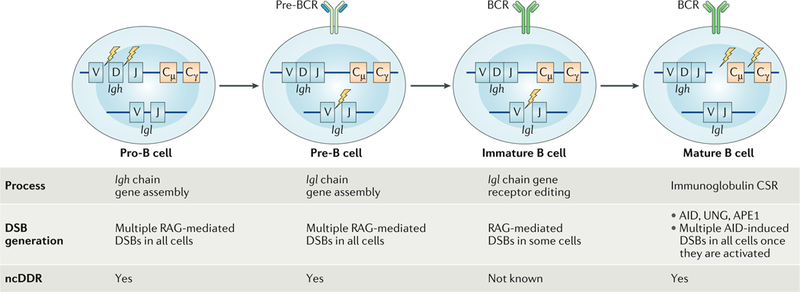
B cell development proceeds in the bone marrow through several discrete steps. From a standpoint of DNA double-strand break (DSB) generation and potential non-canonical DNA damage response (ncDDR) signalling, these stages can be generally divided into the pro-B cell stage in which Igh gene assembly occurs in all cells, the pre-B cell stage in which Igh gene assembly occurs in all cells and the immature B cell stage in which receptor editing occurs in some cells. DNA DSBs are also generated in mature B cells once they are activated and initiate class switch recombination (CSR). AID, activation-induced deaminase; APE1, apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1; BCR, B cell receptor; RAG, recombination-activating gene; UNG, uracil-DNA glycosylase.
