Fig. 5:|. The toggle model.
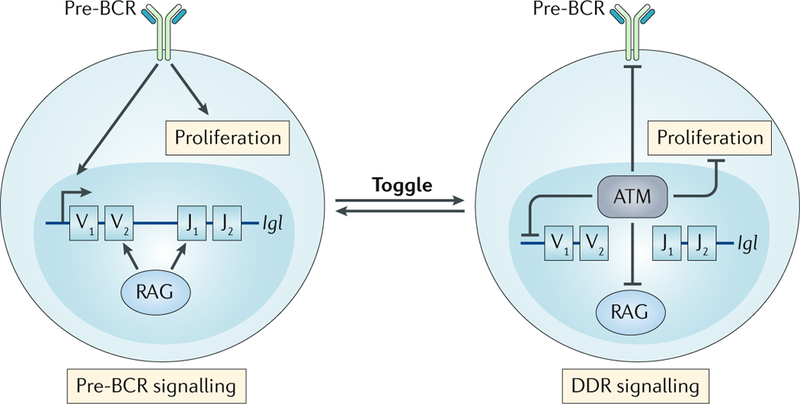
Small pre-B cells have two signalling states; first, pre-B cell receptor (pre-BCR) signalling that promotes Igl gene rearrangement and, second, signalling via ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), in response to double-strand breaks (DSBs) generated by recombination-activating gene (RAG) proteins, that activates a non-canonical DNA damage response (ncDDR). The ncDDR suppresses additional RAG DSBs until the Igl gene assembly is complete and is tested to determine whether it encodes a functional IgL chain. Small pre-B cells may iteratively toggle between these two signalling states as they undergo multiple rounds of Igl chain gene rearrangements in an ordered manner as they attempt to generate a functional IgL chain.
