Fig. 7:|. Activation of the ncDDR in macrophages.
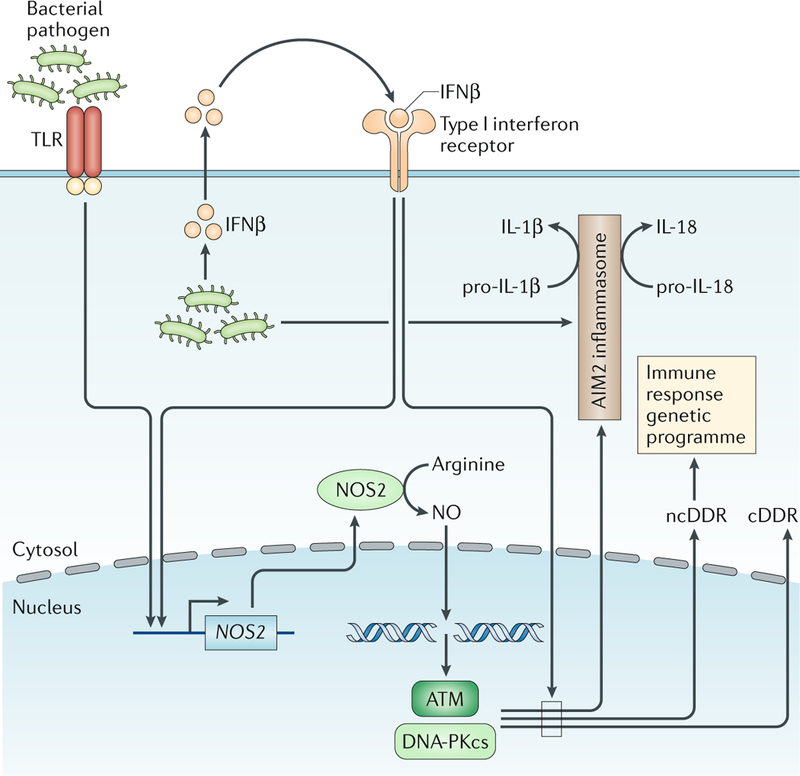
Macrophages activated by signals through Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interferon receptors produce nitric oxide (NO), which causes genomic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) that activate ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs), leading to a canonical DNA damage response (cDDR) and a non-canonical DNA damage response (ncDDR). The ncDDR promotes a broadly functional genetic programme in these cells and regulates inflammasome activation. Type I interferon signals are required for optimal cDDR and ncDDR activation. NOS2, nitric oxide synthase.
