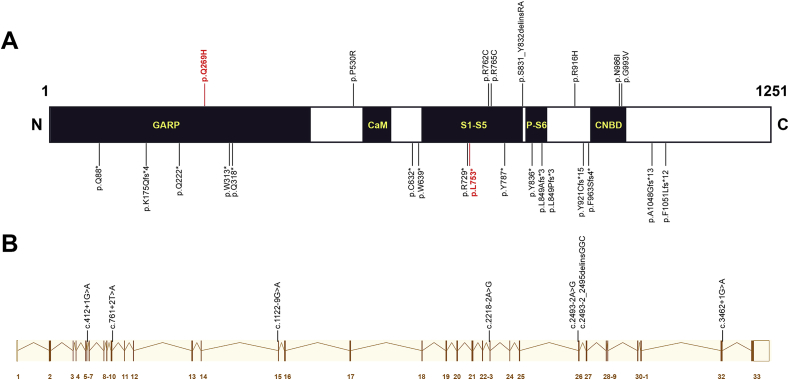
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of the CNGB1 protein (A) from the canonical transcript ENST00000251102 (B) modified from: http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Transcript/Summary?db=core;g=ENSG00000070729;r=16:57882340-57971116;t=ENST00000251102). The CNGB1 gene product has a glutamic-acid rich protein (GARP) domain, a calmodulin-binding domain (CaM), and six trans-membrane domains (S1-S6) including the pore-forming domain (P), and a cyclic nucleotide binding domain (CNBD).16 The previously reported disease-causing mutations are shown on A; top: missense changes including the variant p.[Gln269His] (red); bottom: nonsense and frameshifting mutations including the p.[Leu753*] (red) mutation. (B): the previously reported splice-site mutations are aligned with the CNGB1 exons. . (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)