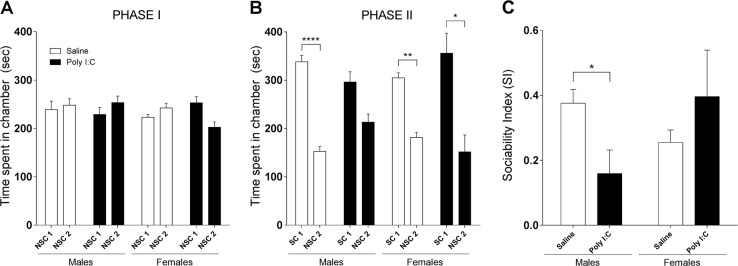
Fig. 3. Prenatal exposure to poly I:C leads to reduced social behavior in males.
Sociability was assessed through the three-chambers test. a PHASE I: time spent in nonsocial chamber-1 (NSC1) versus nonsocial chamber-2 (NSC2) is unaffected by treatment or sex. b PHASE II: time spent in the social chamber-1 (SC1) is significantly higher than time spent in NSC2 for each groups except for poly I:C males. In line with this finding, sociability index (SI) indicates that poly I:C prenatally treated males have a significantly decreased sociability (c). Saline males n = 10; Poly I:C males n = 8; Saline females n = 15; Poly I:C females n = 5. Data expressed as mean ± SEM; Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (a and b), and two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD post-hoc (c) (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001)