Fig. 2.
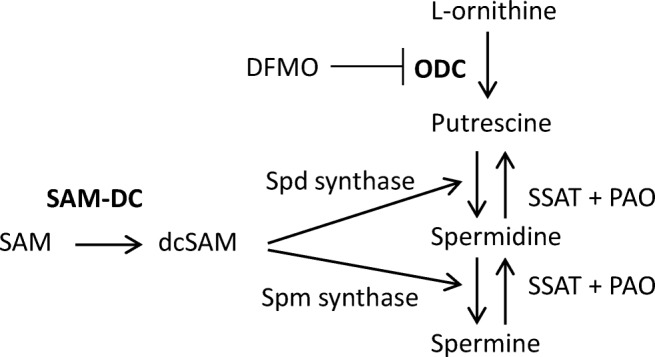
Cellular polyamine pathways. ODC catalyzes decarboxylation of L-ornithine to produce putrescine [NH2(CH2)4NH2]. Two other enzymes are involved in spermidine (spd) synthesis. First, S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (SAM-DC) converts SAM to decarboxylated SAM (dcSAM). Spermidine (spm) synthase then transfers an amino propyl radical (NH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-) from dcSAM to putrescine to produce spermidine [NH2(CH2)3NH(CH2)4NH2]. Similarly, spermine synthase transfers an amino propyl radical from dcSAM to spermidine to produce spermine [NH2(CH2)3NH(CH2)4NH-(CH2)3NH2]. In the catabolic pathway, spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT) first converts spermine to N1, N12-diacetylspermine, which is then oxidized to spermidine by polyamine oxidase (PAO). Similarly, SSAT converts spermidine to N1-acetylspermidine, which is then oxidized to putrescine by PAO. The two rate-limiting enzymes in (forward) polyamine synthesis are in bold
