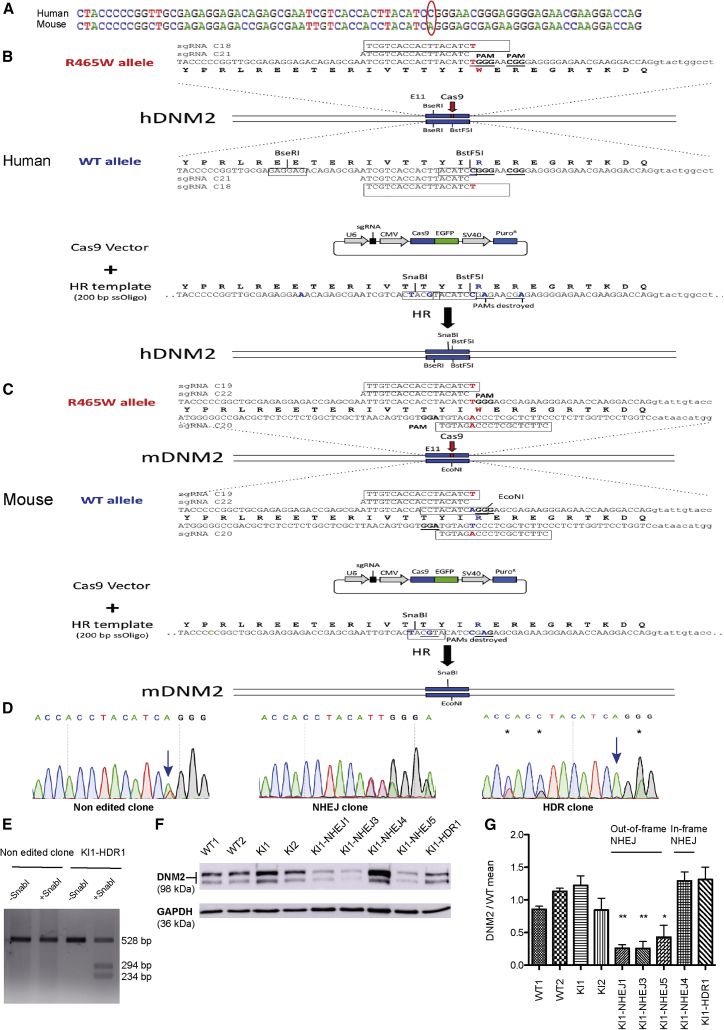
Figure 2.
Strategy and Results for Allele-Specific Inactivation and/or Correction in Muscle Cells
(A) Alignment of the human and mouse WT sequences. The CGG codon in human (top) or the AGG codon in mouse (bottom) code for the conserved arginine residue. In human and Dnm2R465W/+ KI mouse, CGG and AGG codons are changed into TGG encoding a tryptophan. Sequences of the human (B), Dnm2R465W/+ KI mouse (C) mutated alleles, sgRNAs, and repair templates. Note the presence of the NGG protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) near the mutation. We designed allele-specific high-score sgRNAs and pan-allelic sgRNA. (D) Examples of chromatopherograms for a non-edited clone, an NHEJ clone, and a corrected HDR clone from Dnm2R465W/+ KI mouse myoblasts. Positions of the mutated or corrected nucleotides are indicated by arrows and the silent variations introduced by HDR with the repair template are marked by stars. (E) SnaBI digestion of DNA from non-edited and corrected Dnm2R465W/+ KI mouse myoblasts. (F) Dynamin 2 protein levels assessed by western blot from WT (WT1, WT2) and Dnm2R465W/+ KI (KI1, KI2) mouse myoblasts and from Dnm2R465W/+ KI myoblasts edited through out-of-frame or in-frame NHEJ or corrected through HDR. (G) Quantification from three independent experiments of DNM2 protein levels, related to GAPDH from WT (WT1, WT2) and Dnm2R465W/+ KI (KI1, KI2) mouse myoblasts and from Dnm2R465W/+ KI myoblasts edited through out-of-frame or in-frame NHEJ or corrected through HDR. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. No statistically significant difference was noted between WT and KI myoblasts by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. Repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test between KI1 clone and KI1-derived edited clones showed that out-of-frame NHEJ led to a decreased DNM2 level, whereas the in-frame NHEJ clone and the HDR-corrected clone had a normal DNM2 level. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.