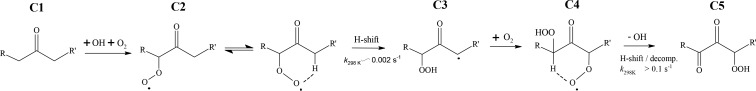
Figure 1.
Autoxidation in OH-initiated oxidation of ketones. Following reaction with OH, the ketone C1 forms a peroxy radical (C2) which undergoes an H-shift isomerization to form a hydroperoxide with a radical center on the carbon atom from which the hydrogen atom was abstracted (C3). Subsequent rapid addition of O2 forms a new RO2 radical (C4), which undergoes another H-shift, in this case terminating the autoxidation process by loss of an OH radical, resulting in a dicarbonyl hydroperoxide. In this scheme, the steps between C2 and C4 define the autoxidation. Adapted with permission from ref (6). Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.