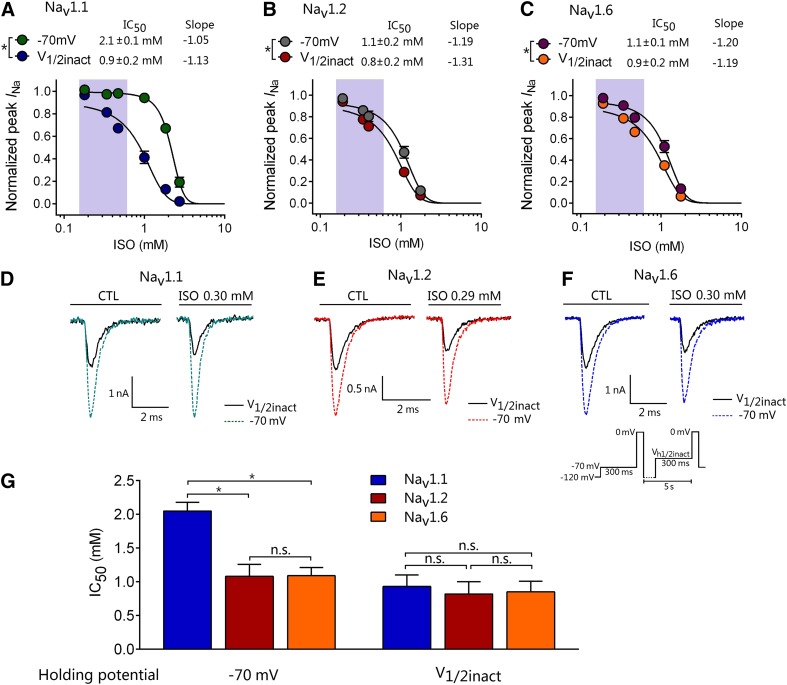
Fig. 5.
Concentration-dependent effects of isoflurane on Nav subtypes. IC50 values for isoflurane inhibition of Nav subtypes from holding potentials of −70 mV or V1/2inact. (A–C) Data for concentration-dependent inhibition of peak INa by isoflurane were well fitted to a Hill equation with significant voltage-dependent inhibition (P < 0.05 by paired t test). The shaded area indicates the clinical concentration range of isoflurane (0.15–0.6 mM; 0.5–2.0 MAC). (D–F) Representative Na+ current traces for the control or isoflurane (ISO). (G) From a holding potential of −70 mV, Nav1.2 (n = 20) and Nav1.6 (n = 17) were more sensitive to isoflurane inhibition compared with Nav1.1 (n = 19). From a holding potential of V1/2inact, IC50 values were similar for all three Nav subtypes. *P < 0.05 by ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni correction. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3–5 for each point). n.s., not significant (P > 0.05).