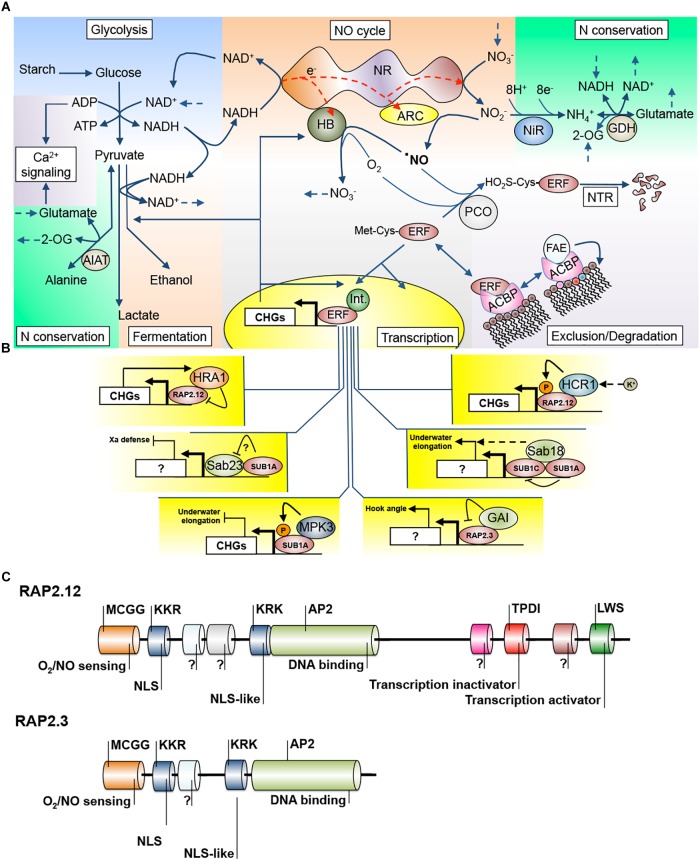
FIGURE 1.
Interconnection of different signaling and transduction events during waterlogging/submergence stress. (A) Integration of metabolic pathways (glycolysis, fermentation, nitrogen conservation and assimilation), hormone homeostasis (NO cycle), calcium-mediated energy signaling (Ca2+ signaling), transcription factor (TF) abundance (N-terminal rule, NTR) and availability (membrane exclusion), and transcriptional control. (B) Known nuclear interactions of hypoxia/anoxia TFs with regulating proteins. (C) Comparison of the domain structure of RAP2.12, a high-complexity ERF-VII TF (the other being RAP2.2) and RAP2.3, a low-complexity ERF-VII TF (others being HRE1 and HRE2), and details of demonstrated domain functions. 2-OG, 2-oxoglutarate; ACBP, acyl-CoA binding protein; ALAT, alanine aminotransferase; ARC, amidoxime reducing component; CHGs, hypoxia core genes; ERF, ethylene response factor; FAE, fatty acid elongase; GAI, gibberellic acid insensitive; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; HB, hemoglobin; HCR1, hydraulic conductivity of the root; HRE1, hypoxia response attenuator; Int., interactor protein; MPK3, MAP kinase 3; NiR, nitrite reductase; NO, nitric oxide; NTR, N-terminal route; PCO, plant cell oxidase; SAB, Sub1A binding.