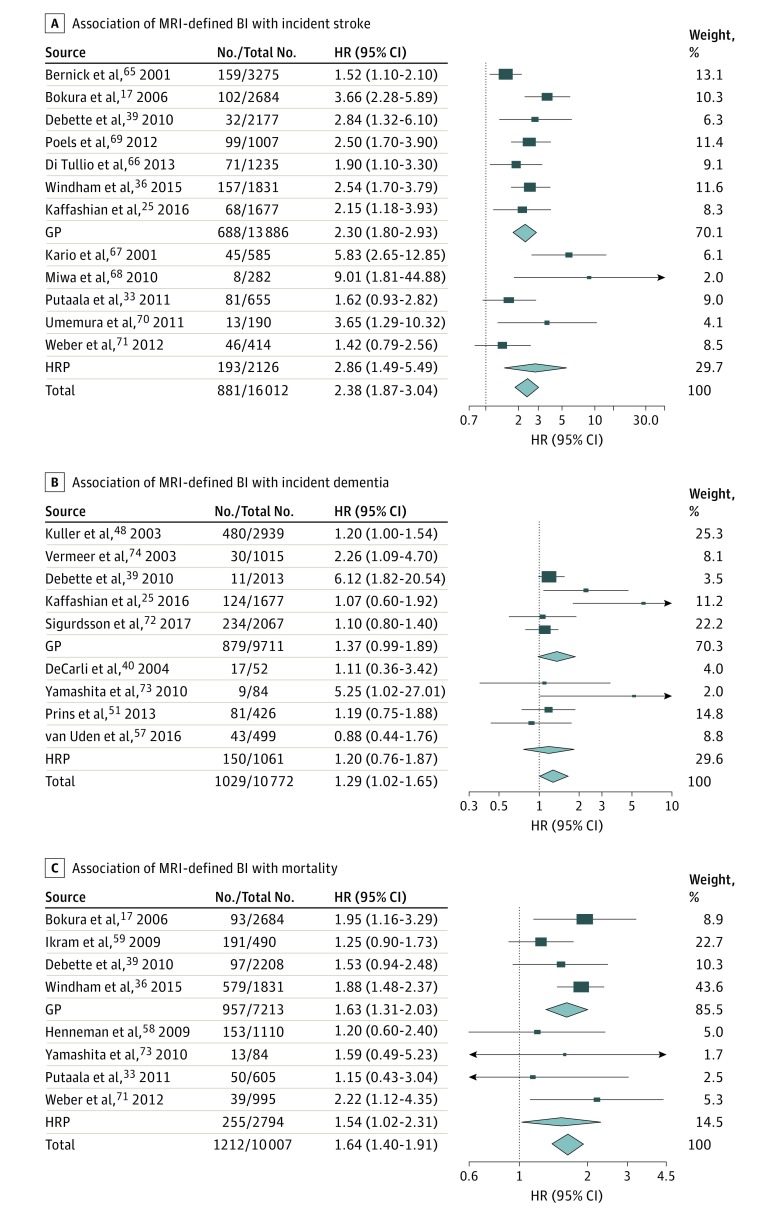
Figure 3. Association of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)–Defined Brain Infarct (BI) With Incident Stroke, Dementia, and Death.
The association of MRI-defined covert BI with incident stroke (A) (overall: I2 = 54%; P = .01; in the general population [GP]: I2 = 45%; P = .09; in high-risk populations [HRP]: I2 = 69%; P = .01), incident dementia (B) (overall: I2 = 44%; P = .08), and mortality (C) (overall: I2 = 0%; P = .48). Results correspond to hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs for each study; the meta-analysis results (inverse variance–weighted meta-analysis with random effects) are shown in diamonds. The No./total No. corresponds to the number of individuals with the outcome of interest and the total sample size.