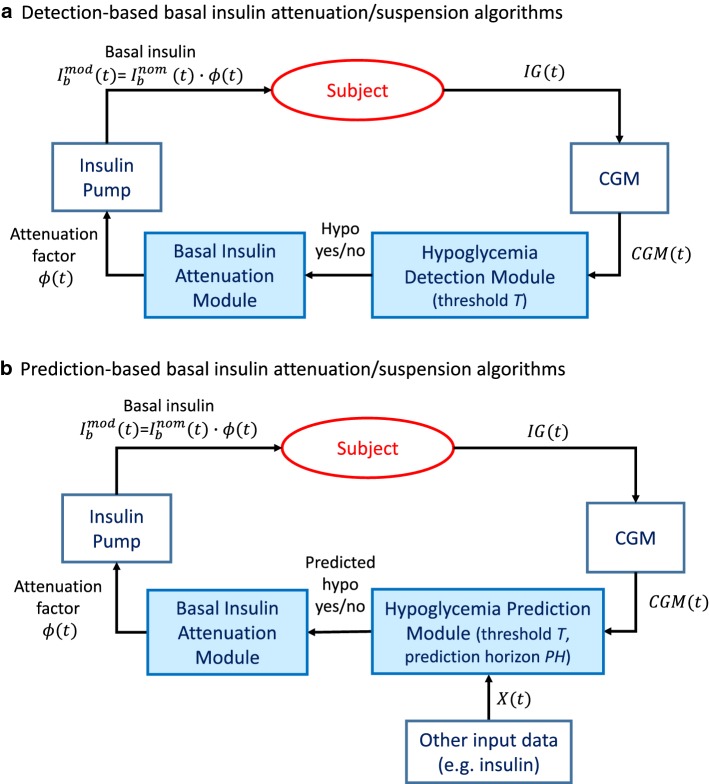
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of basal insulin suspension/attenuation algorithms. a Schema of algorithms based on detection of hypoglycemia. Measurements of subject’s interstitial glucose (IG) concentration are real-time collected by a CGM sensor. When CGM measurements go below a threshold T, the hypoglycemia detection module detects hypoglycemia. Then, the basal insulin attenuation module calculates the attenuation factor , which is 0 if no hypoglycemia is detected and if a hypoglycemia is detected. Finally, the nominal basal insulin delivery rate, , is multiplied for to obtain the final modulated basal insulin delivery rate, , which is given in output by the insulin pump. b Schema of algorithms based on prediction of hypoglycemia. In these algorithms, CGM measurements are used, optionally together with other input data (e.g. insulin), to predict in real-time the occurrence of hypoglycemic events PH min in advance (hypoglycemia prediction module). Such hypoglycemia prediction is then used to calculate a basal insulin attenuation factor, , as in detection-based methods