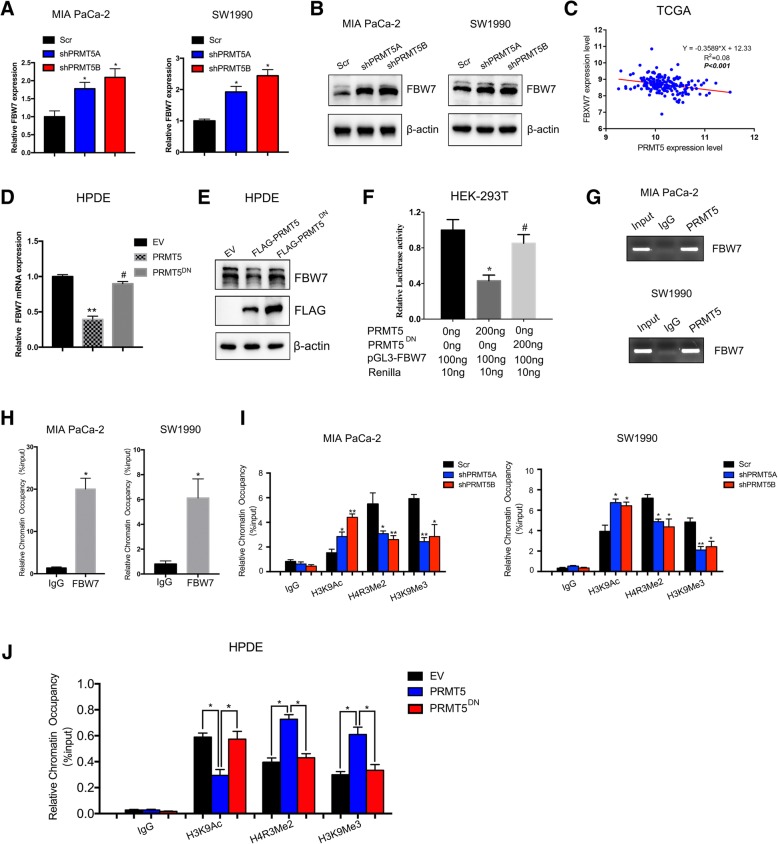
Fig. 5.
PRMT5-mediated epigenetic silencing of FBW7 leads to increased cMyc levels a. In PRMT5-silenced MIA PaCa-2 and SW1990 cells, the mRNA levels of FBW7 were increased. b. PRMT5 knockdown increased FBW7 protein levels. c. PRMT5 expression was negatively correlated with FBW7 expression in the TCGA-PAAD dataset of pancreatic cancer patients. d. In HPDE cells, overexpressing PRMT5 decreased FBW7 mRNA levels, but PRMT5DN did not regulate FBW7 expression. e. Overexpressing PRMT5 in HPDE cells decreased FBW7 protein levels, but PRMT5DN exerted no impact on FBW7 protein levels. f. The results of the dual luciferase assay in HEK-293 T cells showed that although PRMT5 suppressed FBW7 promoter activity, PRMT5DN did not significantly regulate FBW7 promoter activity. g-h. The ChIP assay results demonstrated that PRMT5 occupied the promoter region enriched with CpG islands. i. PRMT5 knockdown decreased the occupancy of the heterochromatin markers H4R3me2 and H3K9me3, and the euchromatin marker H3K9ac, which reflects active transcription, was increased in MIA PaCa-2 and SW1990 cells with PRMT5 knockdown. j. Finally, we performed ChIP in HPDE cells with low PRMT5 expression. The ChIP results showed that PRMT5 increased the occupancy of heterochromatin markers such as H4MR3me2 and H3K9me3 and decreased that of the active chromatin marker H3K9ac decreased. However, the transferase-dead PRMT5DN mutant had no such effect