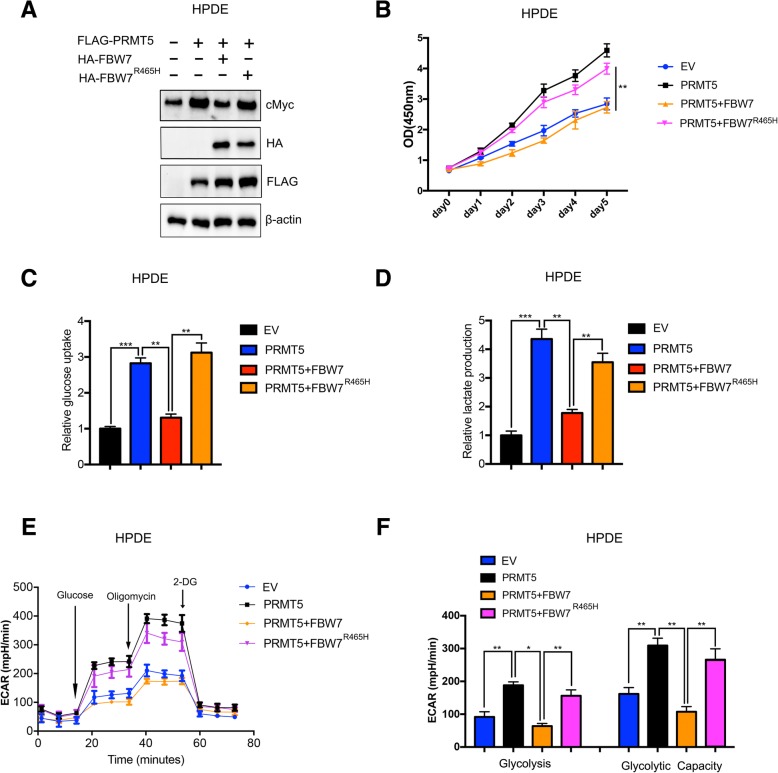
Fig. 6.
PRMT5 regulates proliferation and aerobic glycolysis via the FBW7/cMyc axis a. Overexpression of wild-type FBW7 in PRMT5-overexpressing HPDE cells attenuated the increase in the cMyc protein level, but the FBW7R465H mutant had no such effect. b. The CCK-8 assay results demonstrated that wild-type FBW7 decreased the increase in cell viability caused by PRMT5, while the FBW7R465H mutant, which lacked enzymatic activity, did not. c. FBW7 suppressed the increase in glucose uptake caused by PRMT5 in HPDE cells, while the FBW7R465H mutant did not. d. FBW7 inhibited the increase in lactate production induced by PRMT5 in HPDE cells, but the FBW7R465H mutant had little impact. e-f. The ECAR measurement results showed that FBW7 mitigated the increase in glycolysis and glycolytic capacity caused by PRMT5, but the FBW7R465H mutant did not, suggesting that PRMT5 regulates aerobic glycolysis via the FBW7/cMyc axis