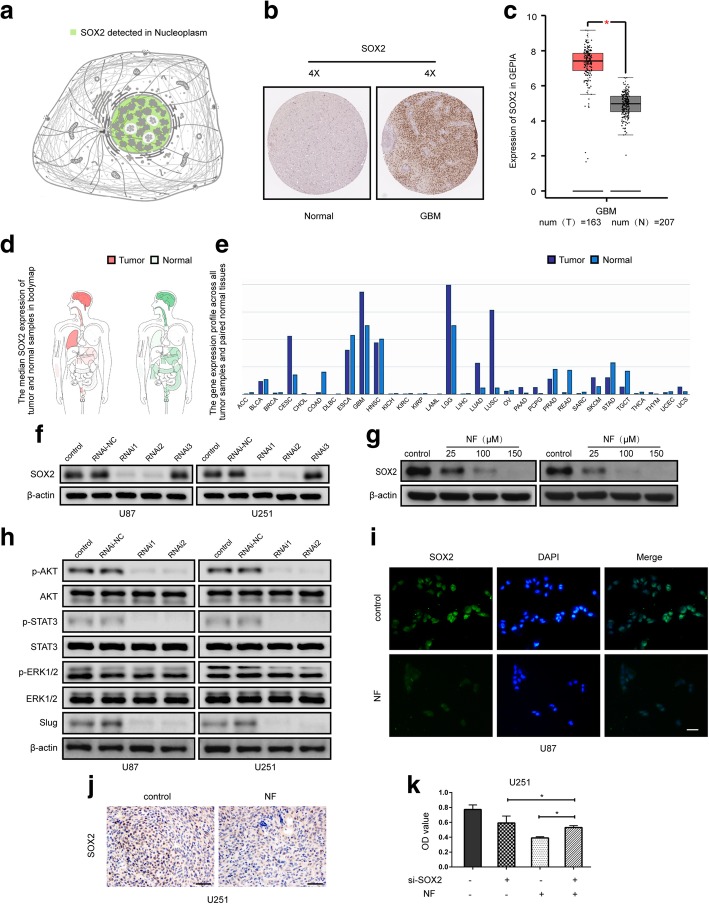
Fig. 6.
SOX2 as a therapeutic target of GBM. a Subcellular localization of SOX2 (The Human Protein Atlas). b Protein level of SOX2 in normal tissue and GBM (The Human Protein Atlas). c mRNA level of SOX2 in normal tissue and GBM (GEPIA). d Median expression in tumor (red) and normal (green) samples in the body map (GEPIA). e mRNA level of SOX2 in 31 different kinds of tumors (GEPIA). f Western blot assay of SOX2 after siRNA transfection using control siRNA RNAi-NC, or SOX2-targeting siRNAs RNAi1, RNAi2, and RNAi3 in U87MG and U251 cells. g Western blot assay of SOX2 after treatment with different concentrations of NF (0–150 μM, 48 h) in GBM cells. h siRNA-mediated knockdown of SOX2 in GBM cells led to significant inhibition of p-AKT, p-STAT3, and Slug. i Immunofluorescence assay (scale bar: 200 μm) of SOX2 after treatment with NF (30 μM, 48 h) in U87MG cells . j Immunohistochemical analysis of SOX2 expression after treatment with NF (15 mg/kg, once a day for a total of 2 weeks) in the U251 xenograft tumors (original magnification: × 400, scale bar: 100 μm). k Insight into a SOX2-dependent mechanism of NF-induced (100 μM, 48 h) inhibition of cell proliferation in U251 cells by MTT assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control group