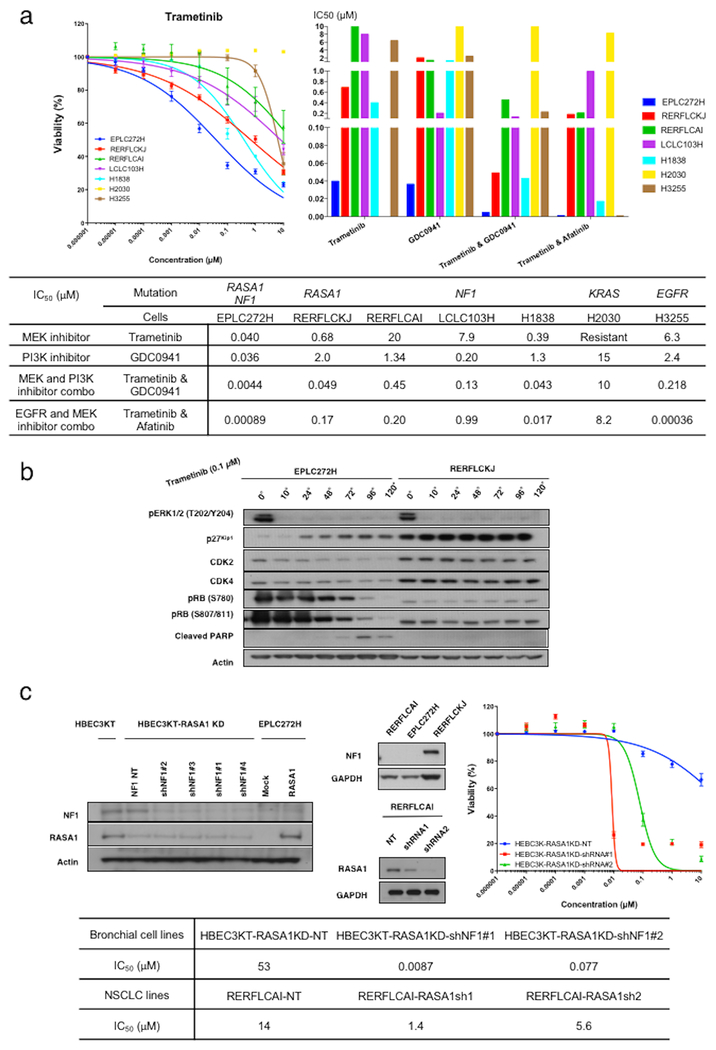
Figure 5. MAPK pathway as a potential target in RASA1/NF1 co-mutated NSCLCs.
(a) A panel of NSCLC lines including RASA1/NF1-co-mutated (EPLC272H), RASA1-mutated (RERFLCKJ), NF1-mutated (RERFLCAI, LCLC103H, and H1838), KRAS-mutated (H2030) and EGFR-mutated (H3233) NSCLC lines were grown in the presence of each drug, and IC50 values were determined using AlamarBlue assay. KRAS and EGFR mutated NSCLC lines were used as control. Error bars denote SEM. The RASA1/NF1-co-mutated cell line EPLC272H was the most sensitive to MEK (trametinib) and PI3K (GDC0941) inhibitors. RERFLCKJ cells were moderately sensitive to MEK inhibitor. Among 3 NF1 mutated NSCLC cells, only H1838 cells were moderately sensitive to MEK inhibitor. NF1 mutated NSCLC cells showed similar sensitivity to PI3K inhibitor. Overall, all cells except KRAS-mutated NSCLC lines showed increased sensitivity to co-administration of trametinib with either a PI3K or EGFR inhibitor. (b) Western blot analyses were performed to analyzed the expression level of key cell-cycle and apoptotic signaling molecules in EPLC272 and RERFLCKJ cells. Elevated p27 and cleaved PARP, and decreased CDK2, CDK4, and pRB were observed only in EPLC272H cells in a time-dependent manner. (c) HBEC3KT cells with RASA1 knockdown were stably infected with non-targeting shRNA (NT) or NF1-targeting sequences (shNF1#1 to #4). Conversely, NF1-mutated RERFLCAI cells were stably infected with non-targeting shRNA (NT) or RASA1-targeting sequences (shRNA1 and shRNA2). Knockdown by each shRNA was confirmed using Western blotting (upper, right and center). The simultaneous inactivation of RASA1 and NF1 induced sensitivity to trametinib in both cell lines (upper, right and lower).