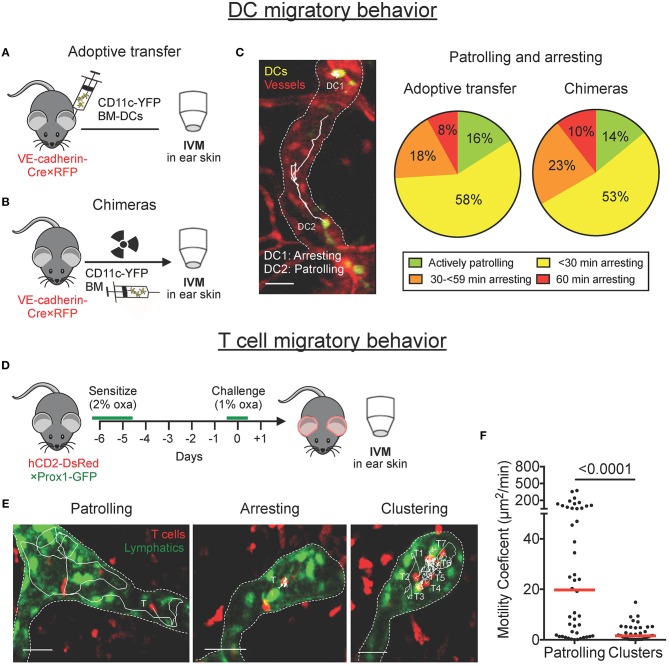
Figure 1.
DCs patrol and arrest, and T cells patrol, cluster and arrest in lymphatic capillaries in mouse ear skin. (A–C) Intravital microscopy was performed in the ear skin of VE-cadherin-Cre × RFP mice in which YFP+ DCs had been adoptively transferred or in bone marrow chimeras. (A,B) Schematic diagrams of the experimental setups. (C) Representative image of YFP+ DC probing and patrolling migratory behavior (scale bars: 30 μm). Tracks of individual DCs imaged over 60 min are shown as solid white lines. Stopping times of CD11c-YFP DCs were quantified manually and classified into four groups based upon their migratory behavior within an imaging period of 60 min. Pooled data from 6–9 mice. (D–F) Intravital microscopy was performed in CHS-inflamed ear skin of hCD2-DsRed × Prox1-GFP mice. (D) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. (E) Representative images of DsRed+ T cells migratory behavior inside lymphatic capillaries (scale bars: 30 μm). Tracks of individual T cells imaged over 30–45 min are shown as solid white lines. (F) Motility coefficient of patrolling T cells and T cells within clusters. Each dot represents a tracked cell. Median is shown as a red bar. Pooled data from 3 mice are shown.