Figure 3.
CTDs with too few or too many consensus heptads are dysfunctional
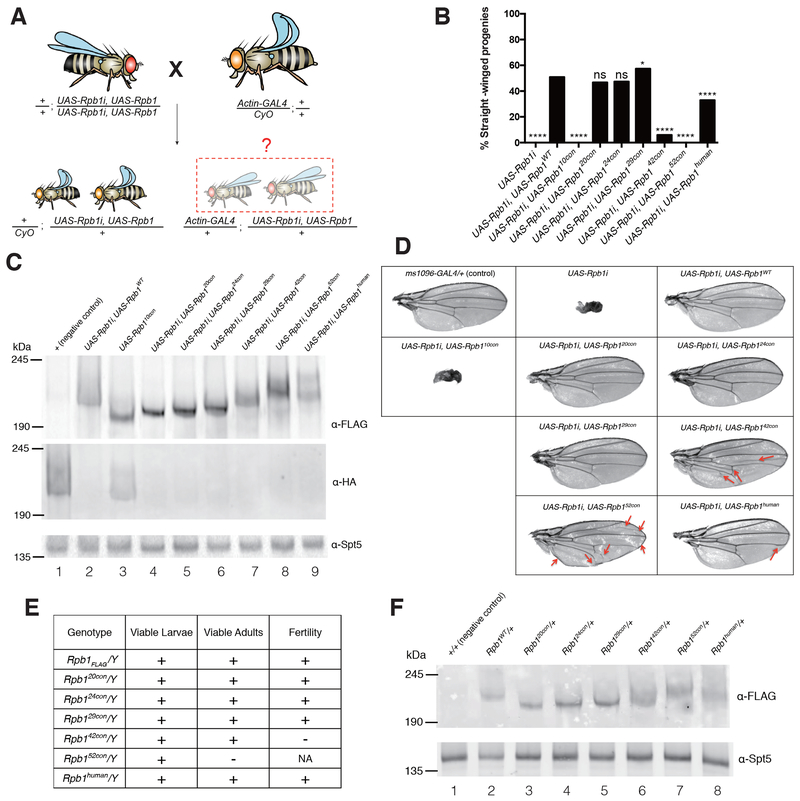
(A) Schematic of the ubiquitous Rpb1i rescue assay. The Act-GAL4 transgene expresses GAL4 throughout development and drives expression of UAS-associated transgenes. UAS-Rpb1i is a GAL4-activated transgene encoding RNAi that knocks down expression of endogenous Rpb1. Rpb1i expression in the absence of ectopically expressed Rpb1 eliminates all straight-winged adult progeny (Act-GAL4/+; UAS-Rpb1i/+). Co-expression of a functional derivative of Rpb1 that has been rendered resistant to the RNAi by synonymous mutations rescues the lethality and yields straight-winged progeny.
(B) Quantification of the results from the Rpb1i rescue assay, n>150 for each genotype. 10con, 20con, 24con, 29con, 42con, and 52con designate Rpb1 derivatives with 10 to 52 consensus heptads. WT designates the wild-type Drosophila CTD and human designates the human CTD. Two-sided chi-squared tests, ns: not significant (p>0.05), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 or ****p < 0.0001 values were considered statistically significant from UAS-Rpb1i, UAS-Rpb1WT.
(C) Western blots of late pupae showing the expression of FLAG-tagged, RNAi-resistant forms of Rpb1 derivatives, and the knockdown of the RNAi-sensitive Rpb1HA. Spt5 serves as a loading control. UAS-Rpb1 and Act-GAL4 were each marked with w+, thus allowing late pupae with Act-GAL4 to be distinguished from their CyO counterparts by an additional copy of w+.
(D) Testing the function of various Rpb1 derivatives in Drosophila wings. Wing-specific expression was driven by ms1096-GAL4. Red arrows indicate creases in the wing or changes in the vein path.
(E) Functionality of CRISPR derivatives of Rpb1 in hemizygous males. The Rpb1 gene resides on the X chromosome.
(F) Western blot showing the expression of FLAG-tagged, CRISPR derivatives of Rpb1 in late pupae. Spt5 serves as a loading control.
See also Figure S2.