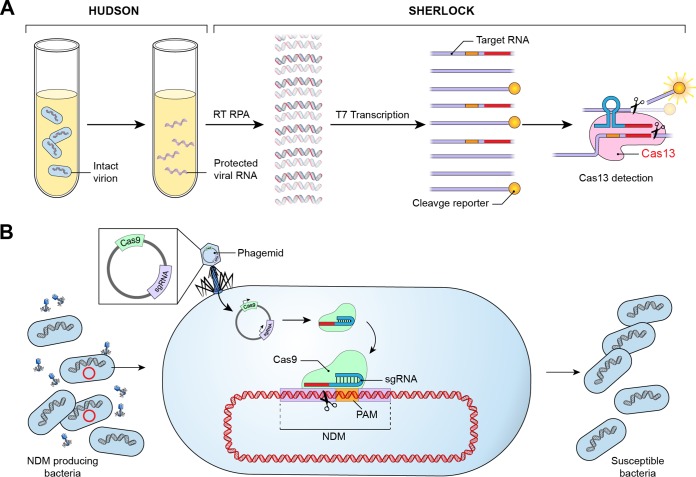
FIG 2.
Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas. (A) A CRISPR-based rapid diagnostic test combines HUDSON with SHERLOCK, allowing rapid detection of viral nucleic acid directly from body fluids. HUDSON employs heat and chemical reduction to inactivate high levels of nucleases present in body fluids and lyses viral particles, releasing viral nucleic acids into solution. SHERLOCK integrates isothermal nucleic acid amplification by RT-RPA with T7-dependent transcription and detection of target RNA through Cas13-mediated cleavage of nonspecific RNA coupled to a fluorescent reporter. (B) CRISPR-based therapeutics include the potential to remove antibiotic resistance plasmids from drug-resistant bacteria. NDM-producing bacteria are transfected with a phagemid containing Cas9 and a sgRNA targeting a spacer in NDM. The sgRNA-Cas9 complex cleaves the NDM gene, resulting in bacteria that are antibiotic susceptible.