Figure 1.
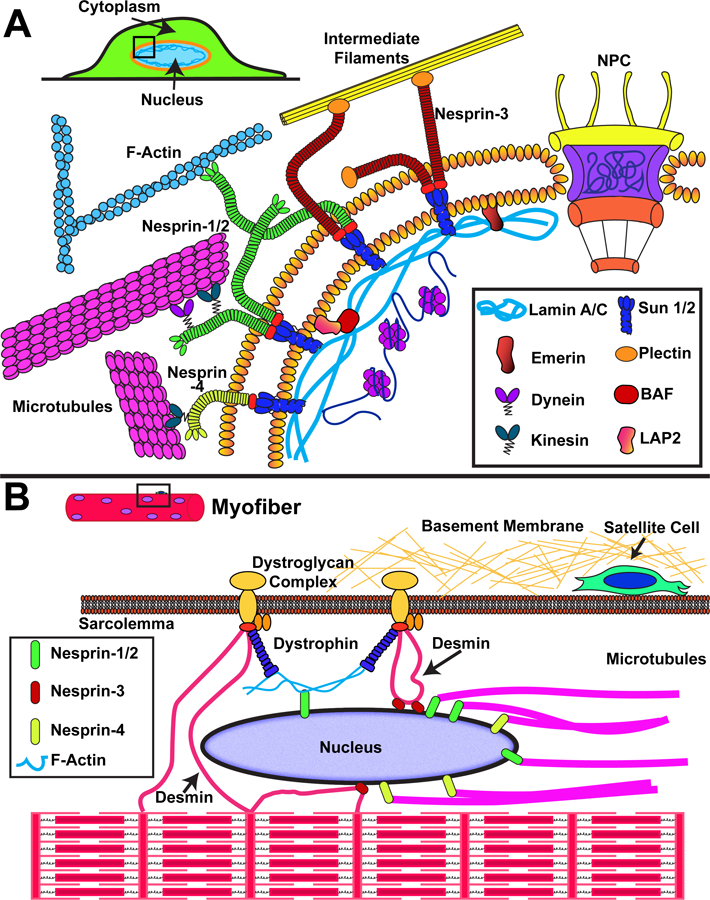
Schematic overview of nuclear envelope proteins involved in force transmission to the nucleus. (A) Force transmission to the nucleus involves interaction of cytoskeletal elements (actin filaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules) with nesprin proteins on the ONM, which transmit force through SUN domain proteins on the INM to the nuclear lamina and interior. (B) Organization of the cytoskeletal network within muscle cells, including the highly ordered actin-myosin structures to form contractile sarcomeres and myofibrils. Nuclei are positioned at the periphery of the cell, where they interact with the muscle-specific proteins dystrophin (through actin filaments) and desmin. Additional proteins such as LINC complex proteins and lamins may be involved in anchoring the myonuclei and place and transmitting forces between the nucleus and cytoskeleton.
