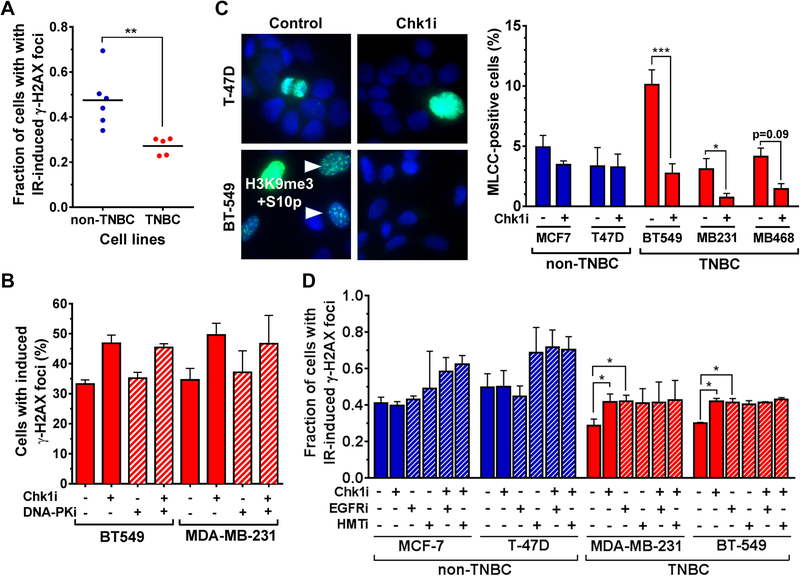
Figure 4. Chk1-dependent radiosensitization correlates with mitosis-like chromatin condensation.
A, Left, comparison of percentage with ≥ 20 IR-induced γ-H2AX foci of non-TNBC and TNBC cell lines 30 minutes following irradiation with 1 Gy. Statistical comparison was performed with the t test.
B, Percentage of TNBC cell lines (BT-549 and MDA-MB-231) with ≥ 20 IR-induced γ-H2AX foci ± LY2603618 and ± DNA-PKcs inhibitor NU7026 (10 μM) initiated 1 hour prior to irradiation.
C, Left panel, representative immunofluorescence images showing co-localized phospho-H3S10 and H3K9me3 marking mitosis-like chromatin condensation (MLCC) [19]. Arrows, punctate interphase-like staining pattern. Diffuse nuclear staining consistent with metaphase. Right panel, percentage of cells with punctuated mitosis-like chromatin staining pattern 30 minutes after Chk1 inhibitor (Chk1i) LY2603618 (100 nM) or mock treatment. Bars represent mean ± standard error based on 3 independent repeats.
D, Fraction of non-TNBC (MCF-7, T-47D) and TNBC (MDA-MB-231, BT-549) cells with ≥20 IRinduced γ-H2AX foci ± LY2603618 (100 nM), ± erlotinib (2 μM), and ± histone-methyltransferase (HMT) inhibitor Chaetocin (100 nM). Bars represent mean ± standard error based on 3 independent repeats.